YouTube & Website Optimization Tips
Video content is one of the indispensable media elements to explain your brand and the service you provide. We are starting our article (on-site video optimization) on how you should position these videos on your website and YouTube platform and how you should provide optimization. Enjoy your reading!
When you add videos to your website, it is very likely that your site performance will improve. When visitors are informed about your product, and your page, they are more likely to spend more time on your site, visit more pages, and generally engage more with your content.
But before you directly upload the video relevant to the page, make sure that the page is not negatively impacted:
Embed YouTube Video on a Page
It is very critical to embed videos on the page so that the video does not negatively affect the size of the page and the page loading speed. In addition, it is very rare for Google to rank the source media file for a video such as .mp4 or .avi. The search engine will almost always rank the page containing the embedded video, whether it is your web page or a channel on YouTube.
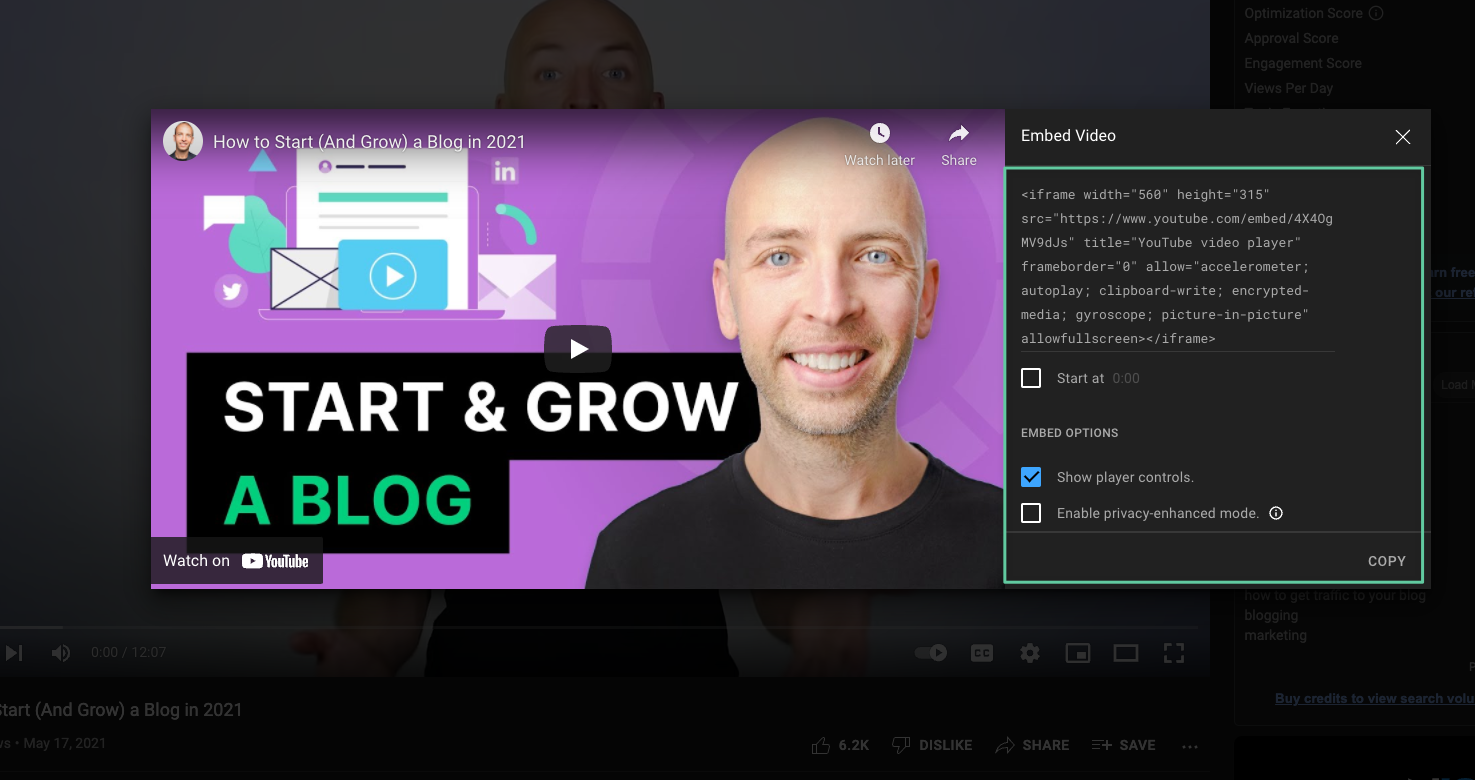
Features such as automatic video playback, annotating, specifying the relevant video size, and starting at the desired second can be set.
In addition, it will be very useful to use attributes such as lazyloading and async to contribute to page performance.
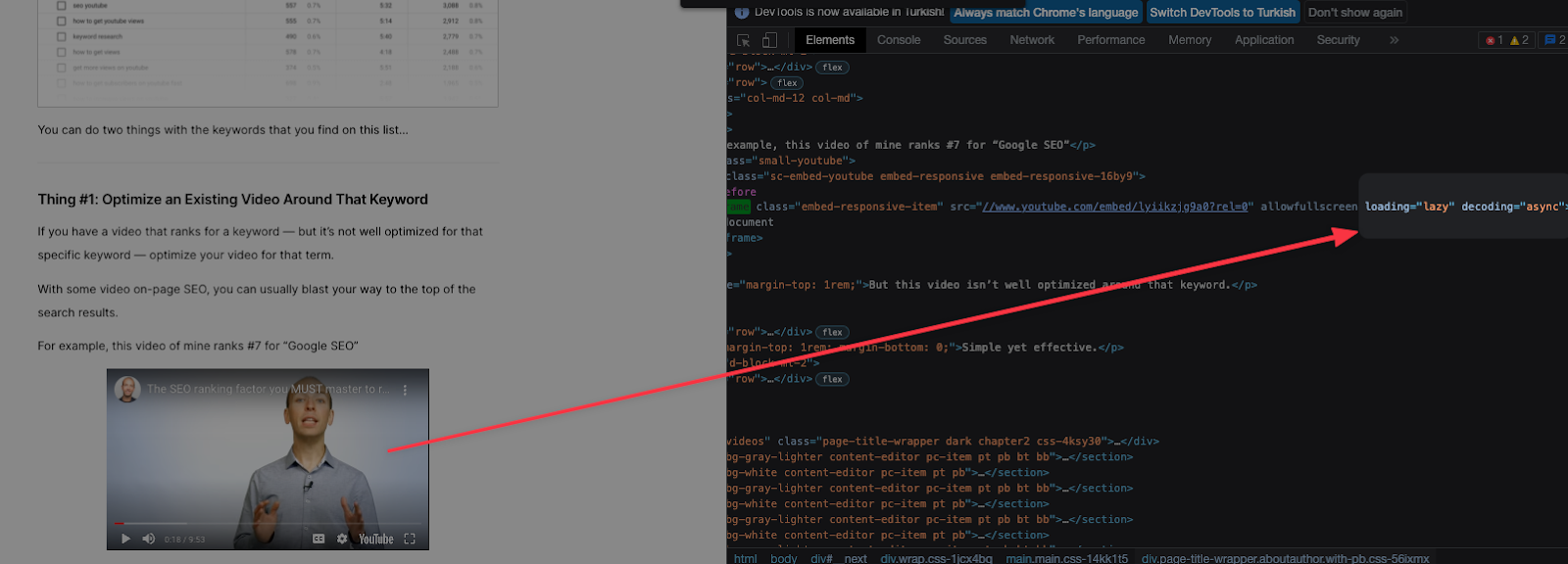
You can check Google's Embed videos & playlists resource for this process.
Optimization Recommendations by Page Type
Video Content Pages
You may have various blog, interview, newsletter, etc. pages on your website where videos are the main content. At this point, it can make sense to put your videos in the above-the-fold area. Showing Google that your video is the primary piece of content on your page will help with performance.
An example of a page positioned as a newsletter under the blog structure, where the main content is video:
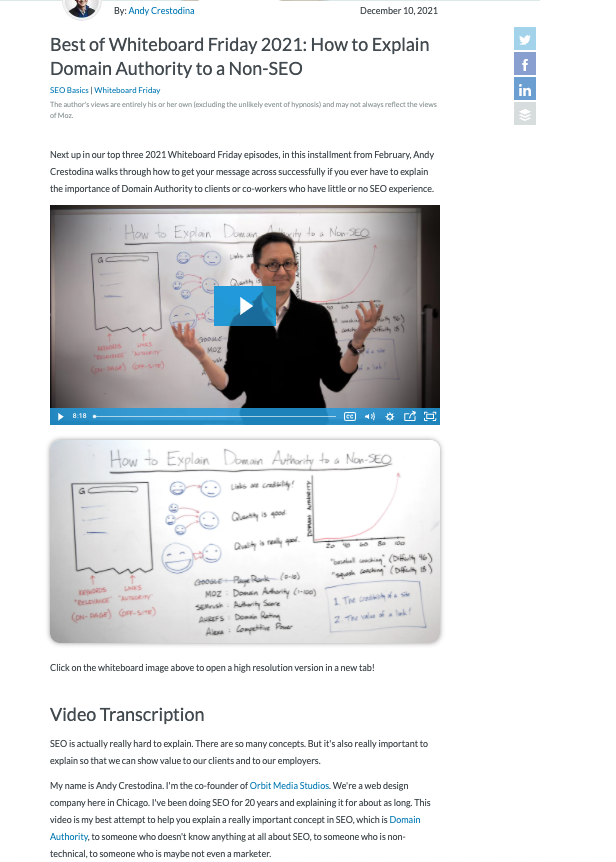
In order to ensure all our optimizations for our custom video pages, we should make sure that the following features are added as much as possible:
- Page Title: This must be the same or very similar to the title of the video.
- H1: Must be the same as the title of the video or be edited to include it.
- Video Description: A summary of the video content written in a way that encourages users to watch the video.
- Video Transcript: The text of the video should be formatted in such a way that users without a voice or with hearing impairments can easily read it.
- Structured Data Markup: The page should have a video type defined using Schema.org markups.
The video transcript is perhaps the most labor-intensive, but very important item in helping Google understand your webpage. A video transcript gives search engines an idea of what your video is about and can potentially help boost your site's rankings. Therefore, it is very important not to skip this item.
https://moz.com/blog/how-to-explain-domain-authority
Pages with Videos as Supporting Content
For example, you can feed a sales-oriented page with a video and explain step by step how you provide this service. Another example is a recipe site, where you might want to explain step-by-step how to make a recipe with a video. When using a video to support the topic of this type of main content, it may require less effort to optimize the page than content pages where the video is the primary content, as the video is not the primary focus of the page. Different optimizations may be required on the video transcript side so that the content doesn't get too long.
For sales purposes, where the video is used as a support and not the main content of the video
a sample page:
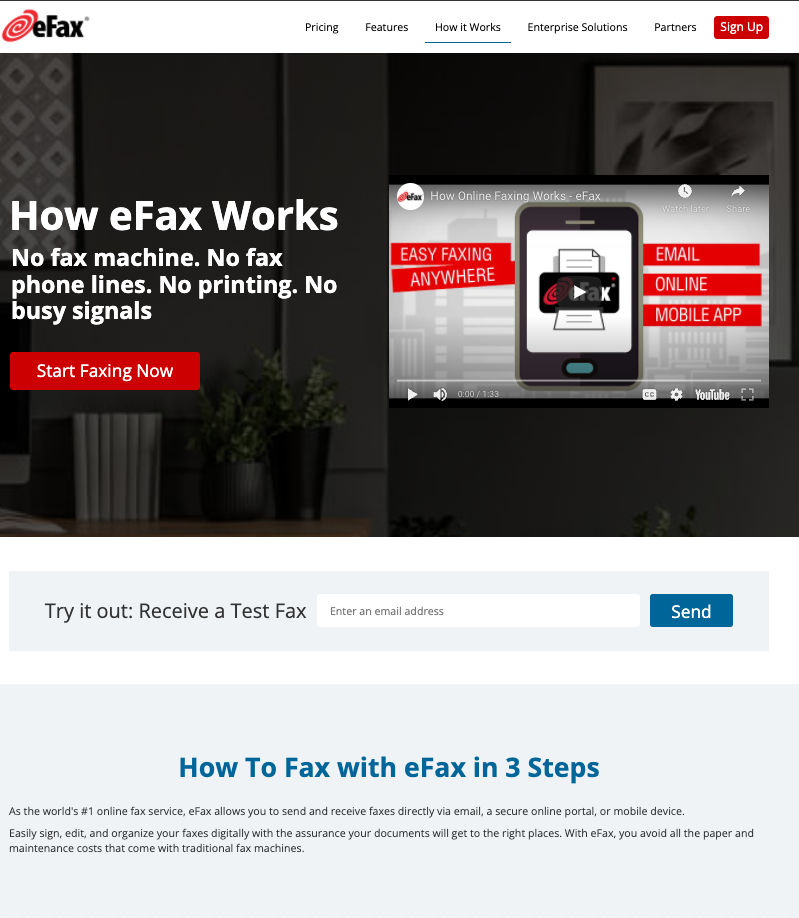
To optimize pages like this for video results, make sure the page has the following features:
- A video description or at least a title: Putting descriptive text next to the video helps users and search engines understand it.
- Video Transcript: This item requires a different optimization than the previous page type. Since the video is not the focal point of the page, a simpler transcript would be more appropriate here.
- Therefore, a few paragraphs of text at the end of the page will work and not distract from the main content.
- Structured Data Markup: As long as a page contains video, structured data markup for video should be used regardless of the page type.
Video Metadata and Structured Data Markup
Since Google can't yet track every video on the web, we need to optimize our videos to explain them and make it easier for them to understand how we use them. One of the most important ways to optimize is structured data markup. In order for our pages to rank in some way, it is necessary to add VideoObject structured data markup type to our pages where videos are embedded.
An example of a VideoObject in the JSON-LD format
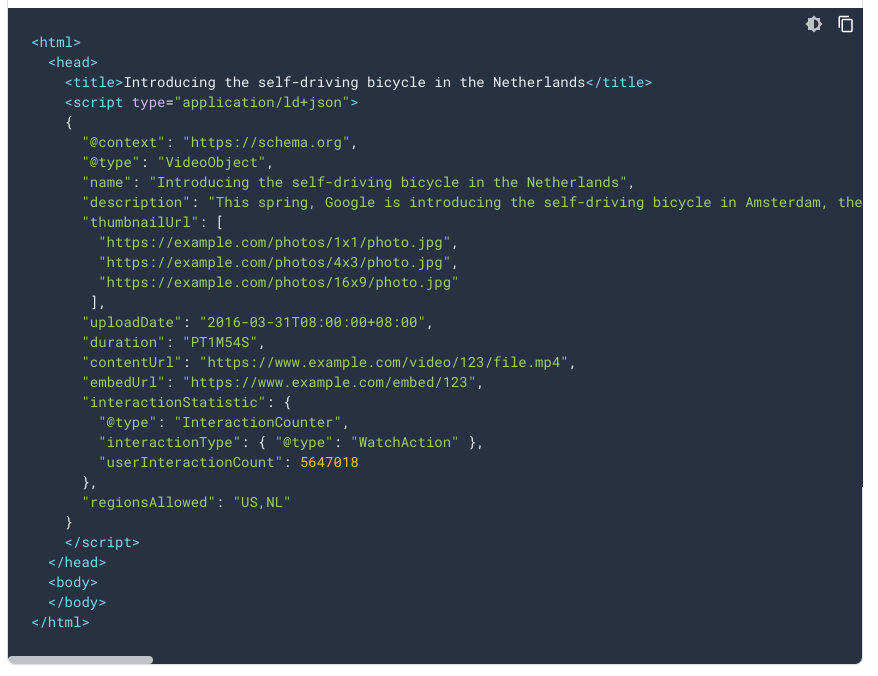
The required properties for the VideoObject structured data type are:
- Description: Written description of the video content. Reuse the video description from the page if it already exists.
- Name: The title of the video. Reuse the same on the page.
- Thumbnail URL: Every embedded video should already have a thumbnail. At this point, either reuse the image URL from the embed code or upload a thumbnail to use for this markup.
- Upload Date: The date the video was first published.
Other important properties recommended for VideoObject types:
- Content URL or Embed URL: If the video has a source media URL on the server or a custom URL that contains only a player for the video, add it here.
- Duration: The video's runtime is in ISO 8601 format.
In this article, we tried to explain many optimization methods related to On-Site Video Optimization. I hope it was a useful resource for everyone. See you in the next content!