Structured Data for AI: Tips for Supporting AI Visibility with Schema
A common question has recently surfaced in the digital marketing and SEO world: How visible are we on AI platforms? Brands are no longer just asking where they rank in Google results, they are questioning how they are perceived and to what extent they are cited by AI-powered search engines, chatbots and AI response systems. While measurement and standards in this field have not yet been fully clarified, it is now clear that certain technical criteria are crucial for AI. Chief among these is structured data, which ensures that content and brands are correctly understood by AI systems. In this blog post, I will discuss the impact of structured data usage on AI visibility and summarize the key actions that can be taken.
What is Structured Data (Schema)?
Structured data (schema) is a standardized markup method that enables search engines to understand the content on a web page more accurately and consistently. It presents the critical information on a page to search engines in a clear and defined format.
This structure, based on Schema.org standards, is generally implemented in JSON-LD format and allows content types such as products, articles, organizations, authors, events, or FAQs to be treated as parsable and interpretable data fields by search engines. In this way, content is handled not just as plain text, but as a classified data structure.
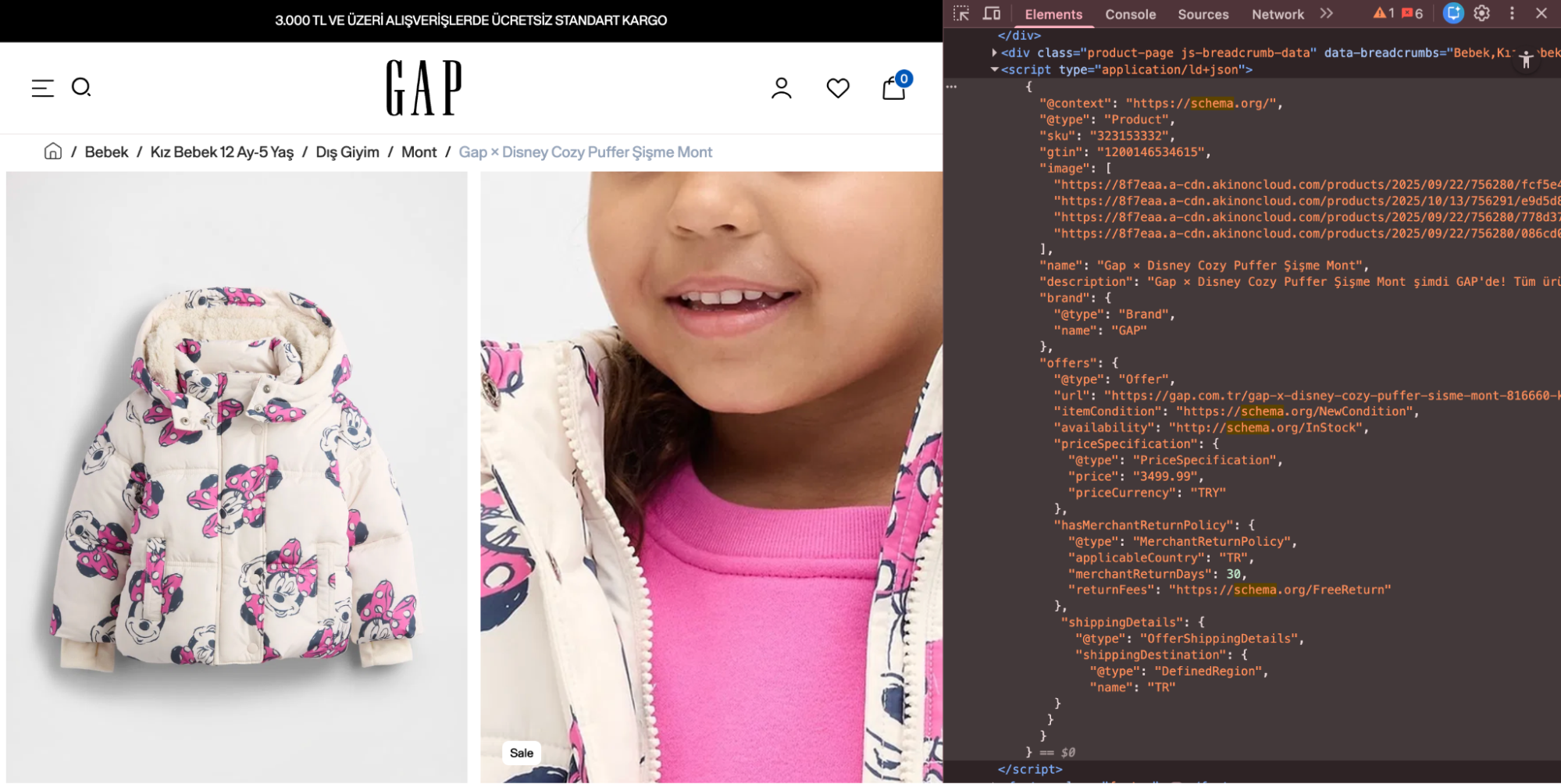
Below, you can see an example of Product Schema defined in JSON-LD format. Within the Schema, product details are specified with elements such as name, description, brand and price.
How Do AI Systems Read Structured Data?
Unlike traditional algorithms, AI systems evaluate data through segmented and semantically tagged entities rather than as a single block. While plain text content can produce different meanings in different contexts, schema markups clearly define what the entities in the content represent. This approach reduces the burden of interpreting text for AI models; it can positively affect AI impressions and increase the likelihood of the content being cited as a reference.
For an AI model to use a source as a reference, it needs to be certain of the accuracy of the information provided and the authority of the source. Schema markups technically provide this certainty through their key-value structure and generate strong contextual signals. Thanks to structured data, content is classified faster, correctly associated with other entities and interpreted consistently. This makes the page easier for AI systems to understand and strengthens its potential to be used as a reliable reference.
The table below summarizes the differences in structured data usage between traditional SEO and AI-oriented GEO:

In short, structured data is no longer just an SEO optimization aimed at obtaining rich results, it is a fundamental requirement for being an understandable, verifiable and citable source for AI systems.
How to Increase AI Visibility Using Structured Data?
1 - Enhancing Product Attributes in Product Schema
While marking up basic fields such as product name, description and price in product schema is now a standard practice, the real differentiator in AI-based search experiences is the level of detail in product attributes. In AI-powered searches, users can create highly specific and intent-driven commercial queries such as “red wool sweater” or “waterproof outdoor shoes.” At this point, rather than pages limited only to basic fields like name and price, clearly and precisely defining differentiating features such as color, material, size and pattern within the schema will help AI systems interpret the page more accurately and produce results tailored to user intent.
For example, when searching for a red sweater on ChatGPT, you can see that details such as material, cut, gender and price are requested as inputs. Therefore, providing these inputs within the schema codes can increase the probability of being cited on AI platforms.
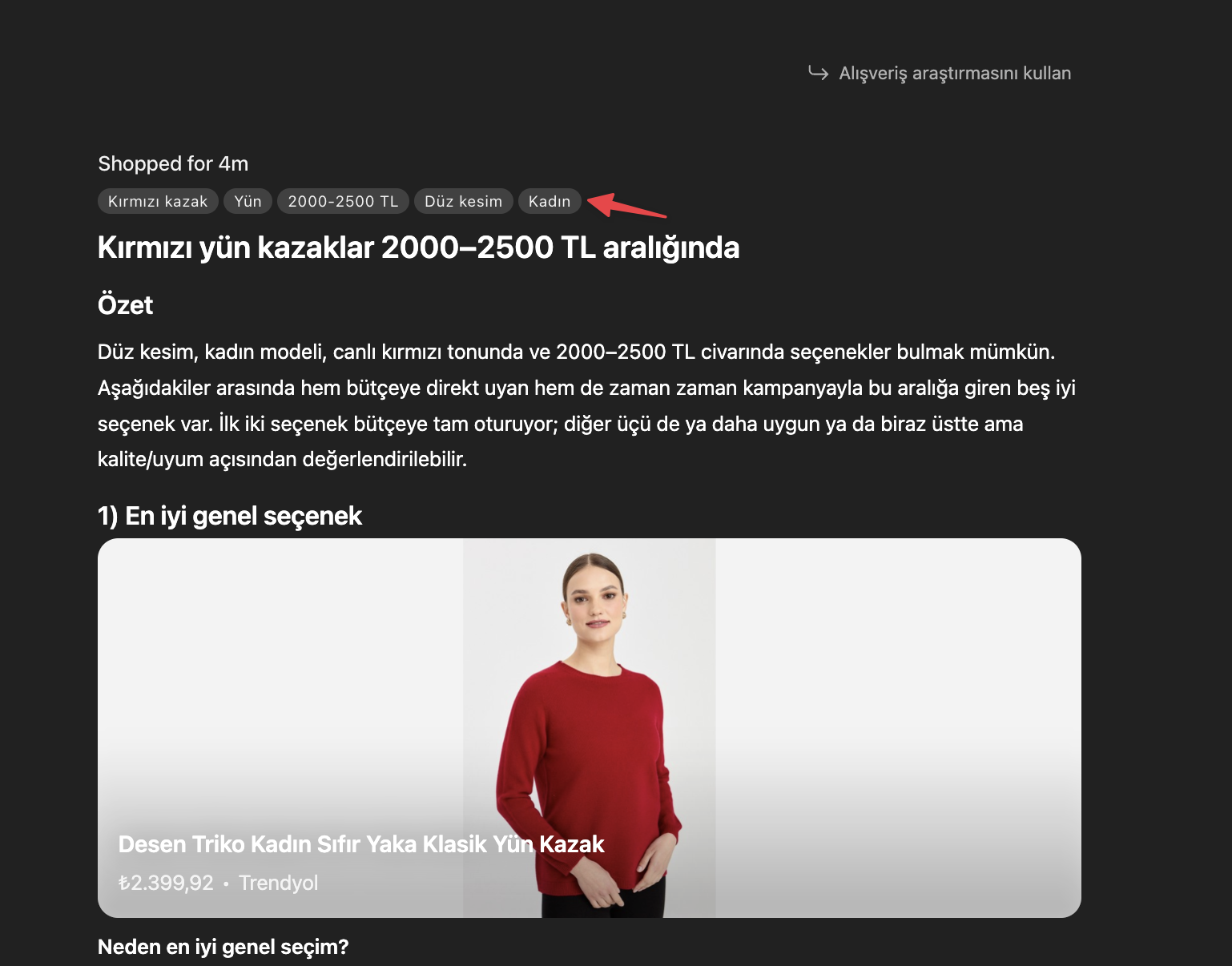
In addition to material information, purchasing decisions and logistical data are also critical in commercial queries. Including information such as availability (stock status) and shipping details in the schema is proof that the product is purchasable and accessible. Therefore, it is highly recommended to use these elements within the product schema. If these fields are missing, products that are out of stock or have unclear shipping options may be pushed down or not shown at all on AI platforms.
Below you can see an example of an advanced product schema.
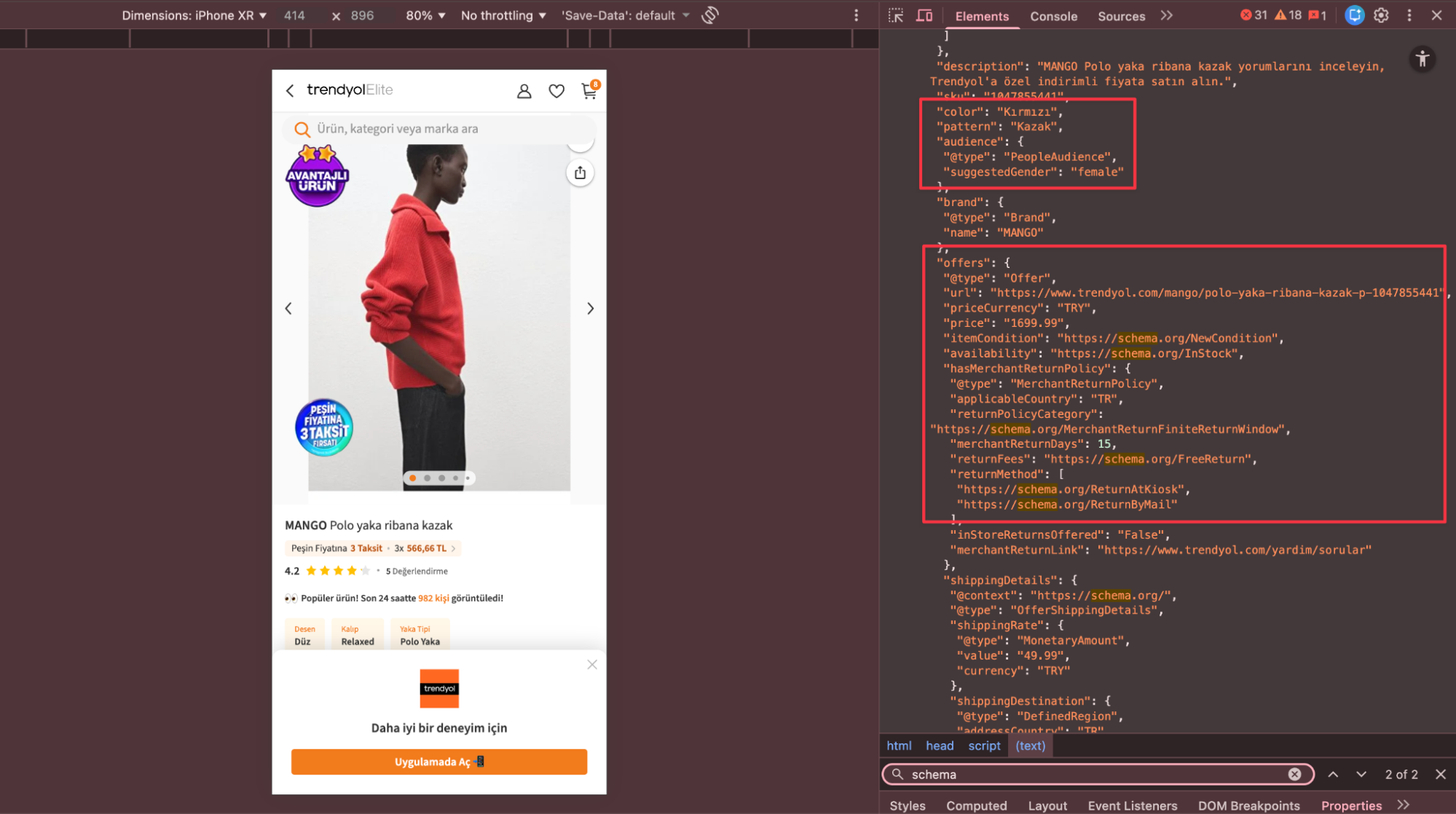
Although comprehensively marking up product attributes does not offer a direct ranking guarantee, it is critical for e-commerce sites to provide this information so that bots can categorize the product more accurately.
2 - Strengthening E-E-A-T Signals for Organization and Person
When evaluating content, AI systems focus not only on what is said but also on who said it and with what authority. We can say that E-E-A-T guidelines are also valid for AI systems to some extent. Therefore, defining digital identity with Organization or Person schema can significantly impact AI visibility.
In Organization schema, instead of just providing a brand name and logo, fields such as legalName, url, contactPoint, address, foundingDate and sameAs should be completed to clearly present the brand identity to AI bots. Especially the sameAs field creates a strong verification layer for AI systems by linking the brand with reliable third-party sources such as LinkedIn, Google Business Profile and Wikipedia. These connections prove that the brand is a defined entity in the digital ecosystem.
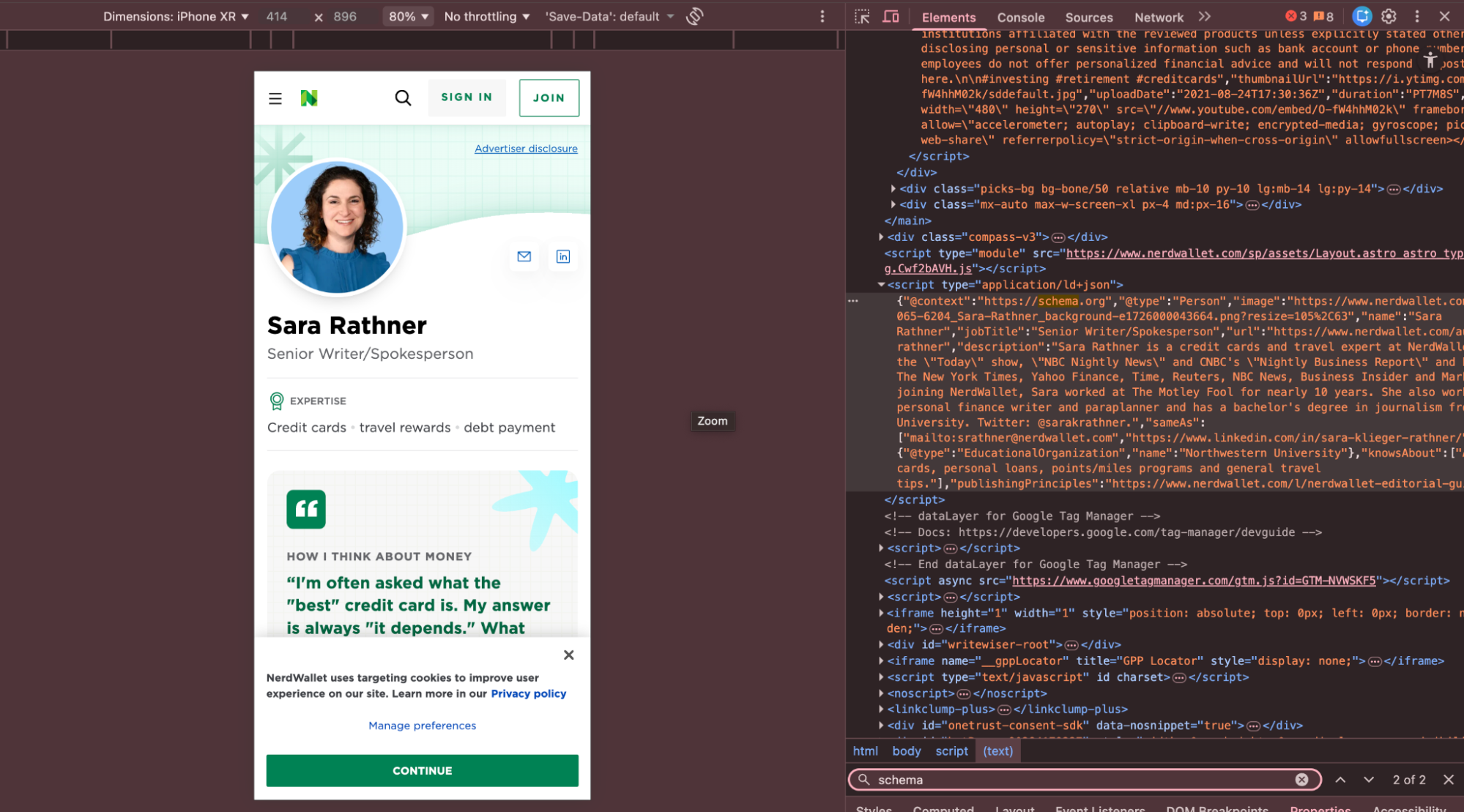
Person schema, on the other hand, is critical for content creators, expert writers and brand representatives. AI systems are more prone to citing content from individuals with defined expertise rather than anonymous or unidentified content. By going beyond the name field in Person schema and using attributes such as jobTitle, worksFor, knowsAbout, alumniOf and sameAs, it clearly demonstrates the author’s areas of competence and the context in which this expertise was formed. This structure makes a decisive difference in AI visibility, especially for finance, health, law and trade content that falls under the category of YMYL (Your Money Your Life).
Below you can find an example of an advanced person schema.
3 - FAQ Schema Usage & Question Optimization
Although Google’s restriction of FAQ rich results has created a perception that this markup has lost its importance, FAQ Schema has made a critical comeback with the GEO process. Users interacting with long-tail queries on AI platforms has turned FAQ schema blocks into one of the most efficient data sources for AI systems.
In this process, rather than building FAQ sections only around keywords with high search volume, it is beneficial to adopt an approach that follows user intent and potential questions more closely. For example, rather than a brand offering marble and ceramic products focusing on a general question like “What is marble?”, it is much more valuable for AI systems to include a clear, scenario-based answer to the question “Is marble or ceramic safer for bathroom floors?” marked with FAQ Schema.
4 - Enriching Article Schema
Article schema is one of the foundational markups that clearly conveys to search engines and AI systems when content was published, when it was updated and by whom it was produced. AI platforms tend to prioritize reliable and verifiable content when determining reference sources. For this reason, pages prepared according to E-E-A-T principles with content, author and publisher information clearly presented in the schema become easier for AI systems to understand and cite.
Especially in rapidly changing subjects such as legislation, pricing, or health, having current datePublished and dateModified fields sends an important signal. Marking updated content with schema meets the AI systems' need to provide the most current and valid information and can increase the likelihood of the content being cited. Similarly, content should not be limited to just the author field, a detailed profile page should be created for the author and supported with Person schema. Marking the author's field of expertise, their institution and their reliable third-party profiles strengthens the author's authority and can help this individual’s content stand out on AI platforms.
5 - Using Speakable and VideoObject Schema
AI models can now process different data types such as audio, image and video simultaneously, rather than just text. This development makes it technically necessary to mark content not only as readable but also as listenable and watchable. By using Speakable schema to define the most crucial parts of the content as speakable for voice assistants and AI systems, content can be prioritized in voice search results and AI assistant responses. This signal reinforces brand authority, especially in guide content intended for fast information consumption.
The role of video in AI strategy takes on a much more critical dimension with VideoObject schema. Instead of spending time analyzing a video's content, AI systems can directly understand what is being explained at which second of the video through fields such as hasPart or key points within the schema. Structuring videos this way increases the likelihood that an AI will reference a specific part of your video as a direct solution in its responses. This approach ensures your content is positioned as a rich and accessible source of information rather than just a wall of text.
6 - Schema-Content Consistency
For structured data to be perceived as a trust signal by AI systems, the content visible on the page must match the data in the code. AI models perform data validation from multiple sources to minimize the risk of hallucination. If a price, technical specification, or author information in your JSON-LD code differs from the visible text on the page, this can create a contradiction for AI systems and negatively impact AI visibility. Therefore, the visible text and the schema must be consistent.
7 - Format Preference
While there are different methods like Microdata or RDFa for adding structured data to your website, JSON-LD is undeniably the most recommended format for AI systems and modern search engines. This format, which Google also officially supports and prioritizes, has become a technical standard in AI visibility strategies.
Since JSON-LD provides a clean block of data independent of HTML code, it allows AI bots to process content much faster and more accurately without being hindered by design complexity. This structure can increase the probability of your brand being perceived as a reliable reference by enabling AI models to easily establish semantic links between data points.
In short, structured data is no longer just a technical application that supports SEO, it is a fundamental condition for being correctly understood by AI systems and positioned as a reliable source. Although limited measurement tools hinder the provision of clear data in this area, a clean and understandable code structure will make it easier for AI bots to interpret the website, just as it does for primary search engine bots like Googlebot. Therefore, by implementing schema optimization, you can take action to increase your AI citations before your competitors do.