The 14 Most Common Redirect Mistakes in SEO
When many SEO issues are not taken into consideration when redirects are made, you may encounter situations such as wasting the crawling budget along with position losses. In this article, I have brought together the most common problems I encounter in redirect setups.
Redirects are an inherent issue of the web after many situations such as the creation of new pages over time, migration processes, subdomain/subfolder changes, and CMS innovations. Redirects can be a few URLs or thousands of URLs can be subjected to these redirection processes. WordPress, Shopify, or different CMSs may also have plugins for these.
You can see the most common problems with subheadings below:
Do Not Always Choose 301 Redirect
The most common redirect is of course the 301 redirect, but maybe your pages need 302, 307, 308, Javascript or a different redirect code instead of this redirect code. Here you should really think about the redirect code required for URLs and adjust your redirects accordingly. If you are going to redirect with 301, you may prefer a server-side redirect.
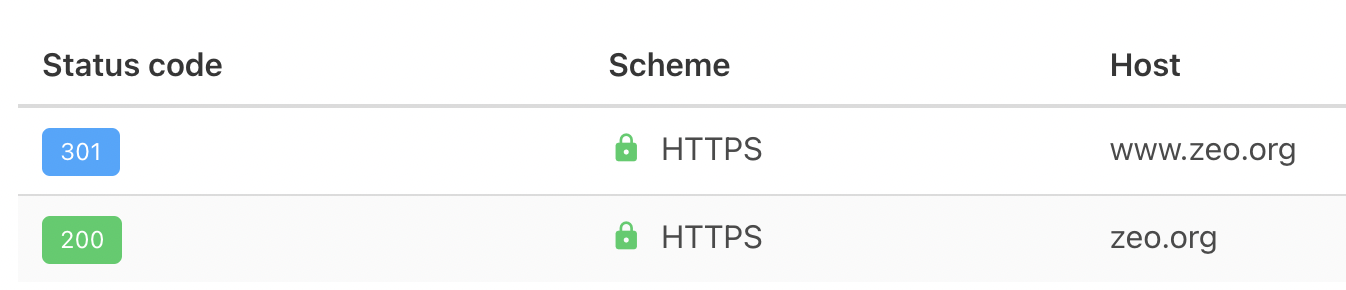
You can use a 301 redirect if you think your URLs really need to be permanently redirected. A 302 redirect indicates that the page is temporarily redirected. In other words, you can redirect with this code in cases where you say "this page is temporarily redirected, but this redirection will end soon".
Redirecting All Pages to Home Page
Don't completely redirect all your URLs, or the majority of pages in the old URL list, to the homepage. Google's John Mueller has already pointed this out in the past, saying, "Redirecting everything to the homepage only is a really bad practice, because we lose all the signals associated with the old content."
If you take this action for pages where you rank well, you could lose traffic and prevent search engines from fully recognizing old data.
Redirect Chain!
When a page is exposed to multiple redirects, both the user and Googlebot may be exposed to extra redirects. In this case, it would be correct usage to redirect each URL with a maximum of 1 redirect.
For example, in cases such as /zeo-old-redirect > /zeo-old2-redirect > /zeo-new-redirect, redirect chains are formed.
You can detect these errors on your site with many crawlers. For example, with Screaming Frog, you can see the related problems if these problems exist on your site and you can find these URLs in the source code and replace them with the final URLs:
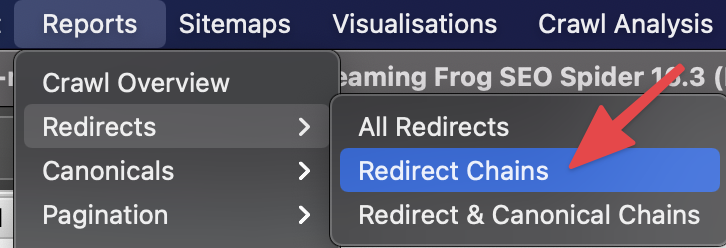
If URLs do not redirect with more than 5 redirects, then Google may stop tracking the URL.
Case Sensitivity
For Google, capitalization or lowercase letters in the URL are seen as separate pages. For this reason, you can create your URLs in lowercase if possible and automatically redirect them to the same pages, considering the situations that may occur with uppercase. You can quickly optimize here with the .htaccess file. Example usage:
Redirect 301 /ekibimiz https://zeo.org/yeni-ekibimiz [NC]
With just a one-line command, users will be directed to the correct page when they use even capital letters.
Accuracy of Routing
When making your redirects, you should always examine whether the old URL is actually redirecting to a new relevant URL. For example, your LP related to /camp-chair should not be redirected to a partially irrelevant page such as /camp-tents. In this case, you will be sending an irrelevant signal to Google.
Search Console Reports
You should definitely examine the reports on referrals, which are important for Google, but not for crawlers. Here you can identify many issues that are overlooked and important for you:
Referred URLs in Sitemaps
You can ensure that your sitemaps include URLs that do not contain redirects. This will help Google identify new URLs faster and index them more easily.
I recommend that the News-Sitemap should be free of these problems, especially for sites with news content.
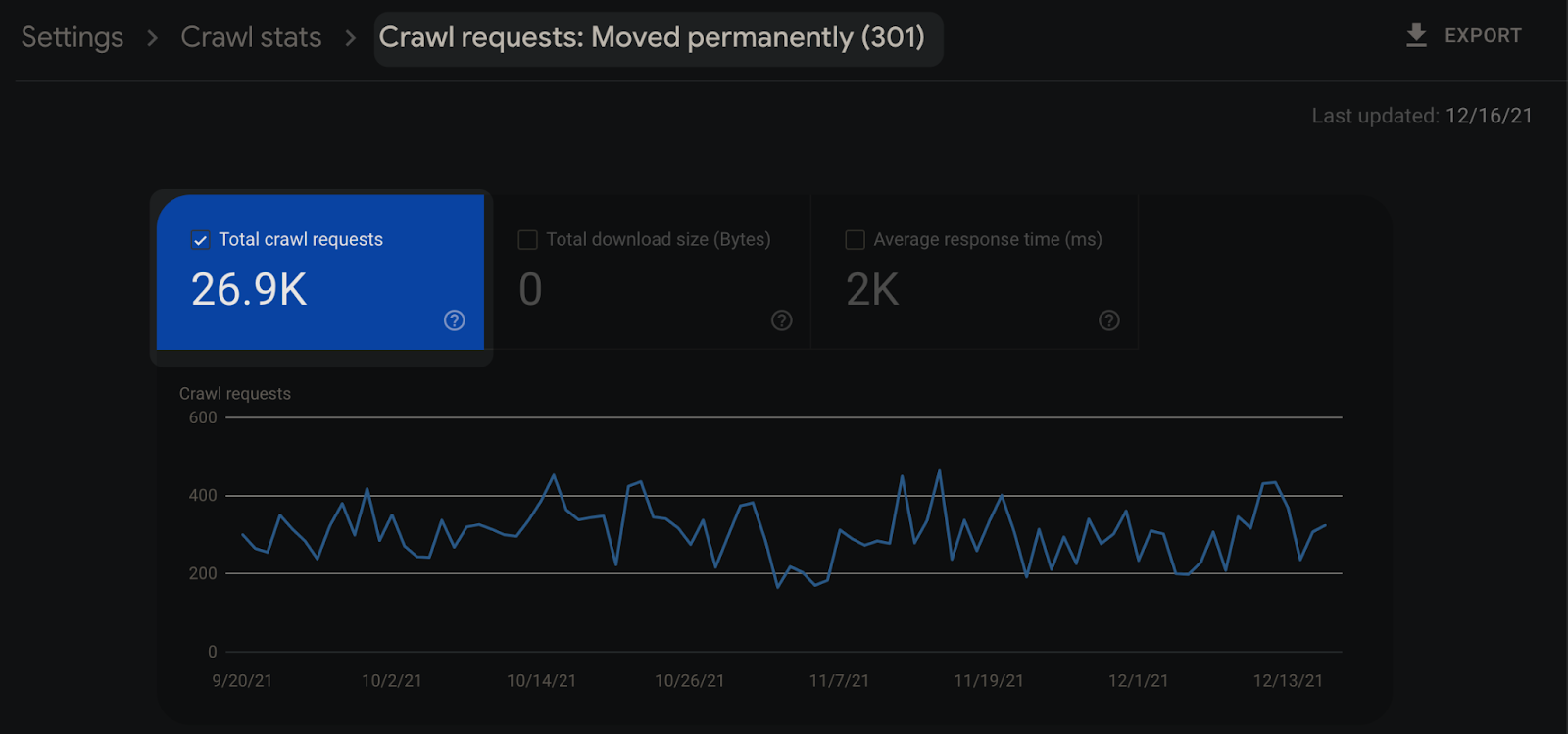
Ignoring Browsing Statistics
It is important to examine URLs with 3xx redirect code in server logs with Google Search Console to optimize the crawl budget:
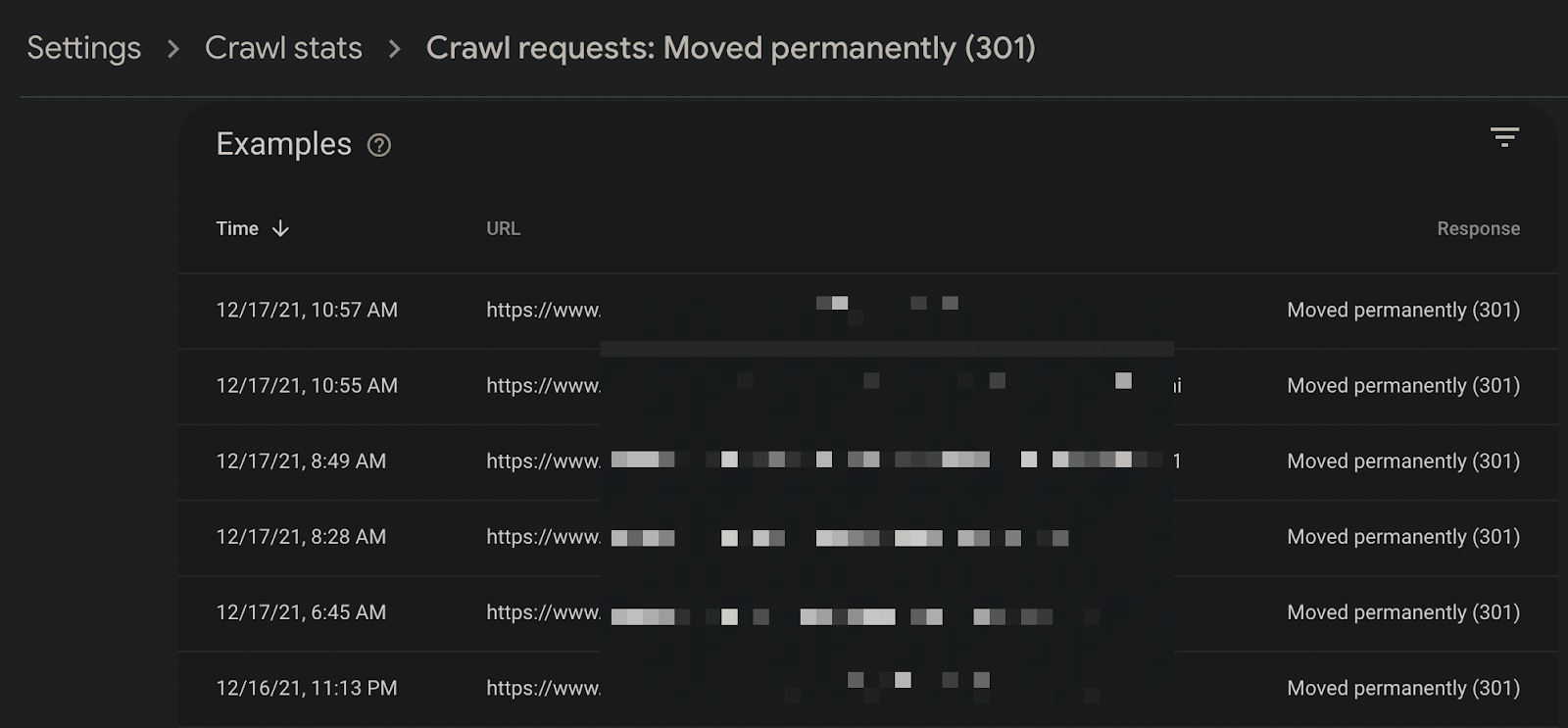
You can also drill down into the URL details to see if pages should actually be redirected:
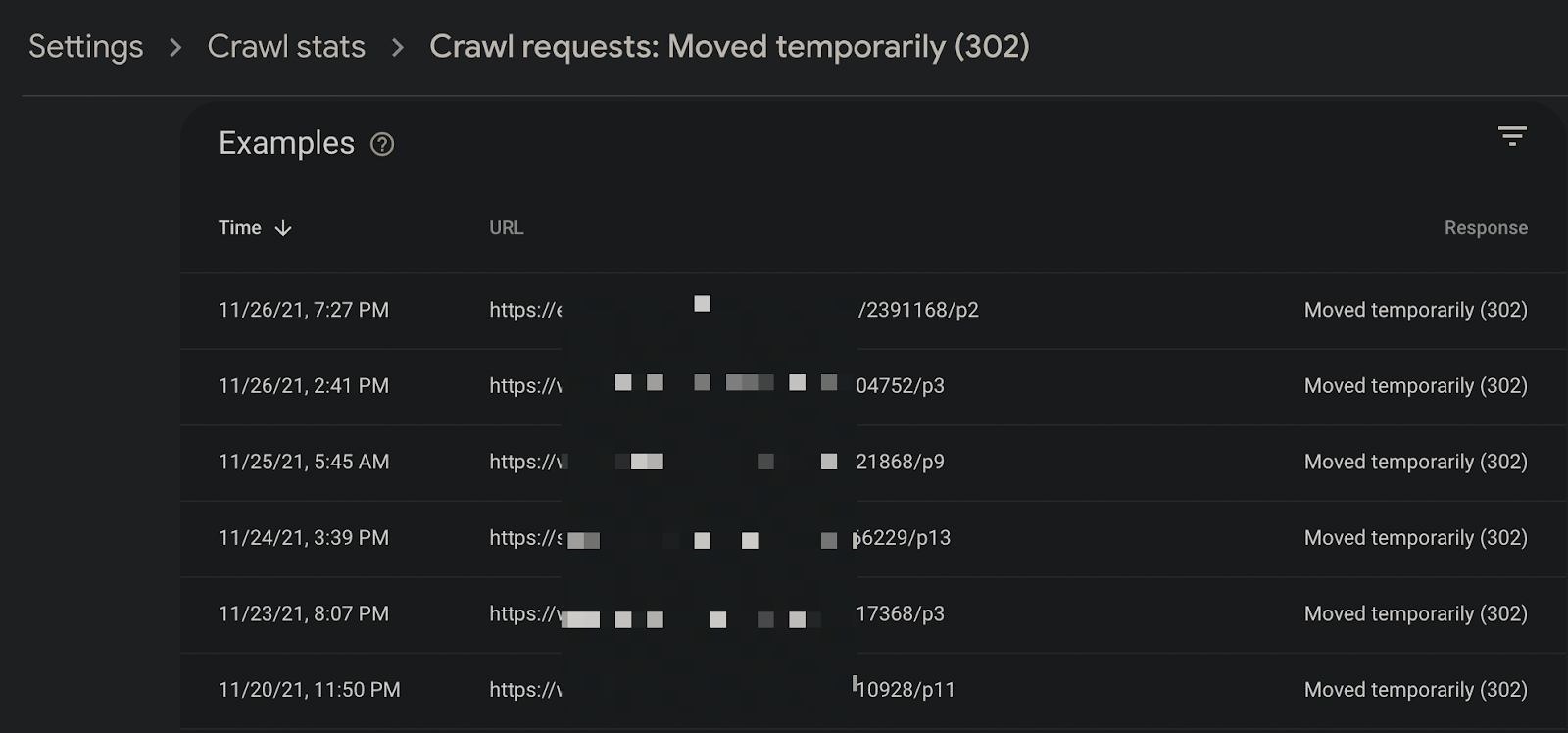
You can also examine whether 302 routing codes should really be routed with 302:
Checking Internal Links
If there are redirecting links within the site, I recommend that you identify them and replace them with new URLs. In this way, you can improve your most linked pages in the in-site link structure and enable Googlebot to crawl the pages with less redirection:
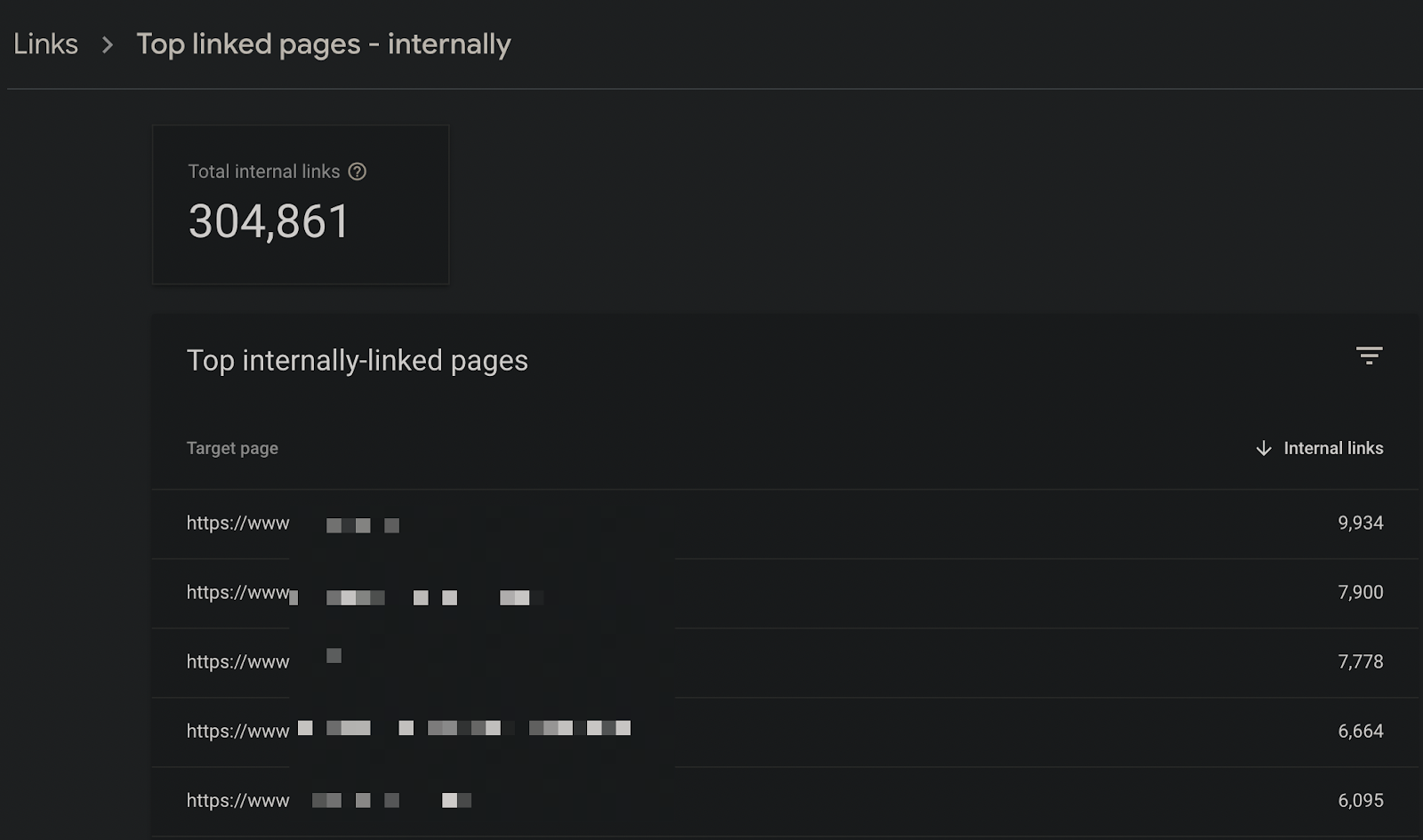
You can pay attention to these situations, especially in internal links in the content used in the blog or category description.
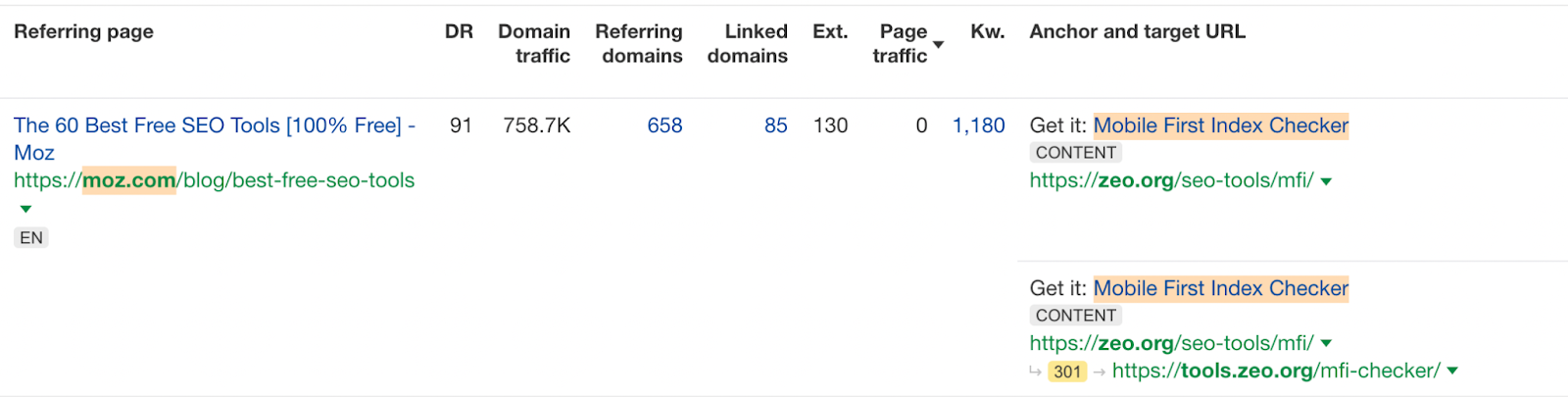
Anchor Texts
You should also make sure that the anchor texts of the redirected pages make sense with the final pages. For example, you should make sure that the links you provide with the anchor text "children's coat" point to the page in the final URL that points to the children's coat. Unrelated uses will make it difficult for Google to understand which page to list in this query.
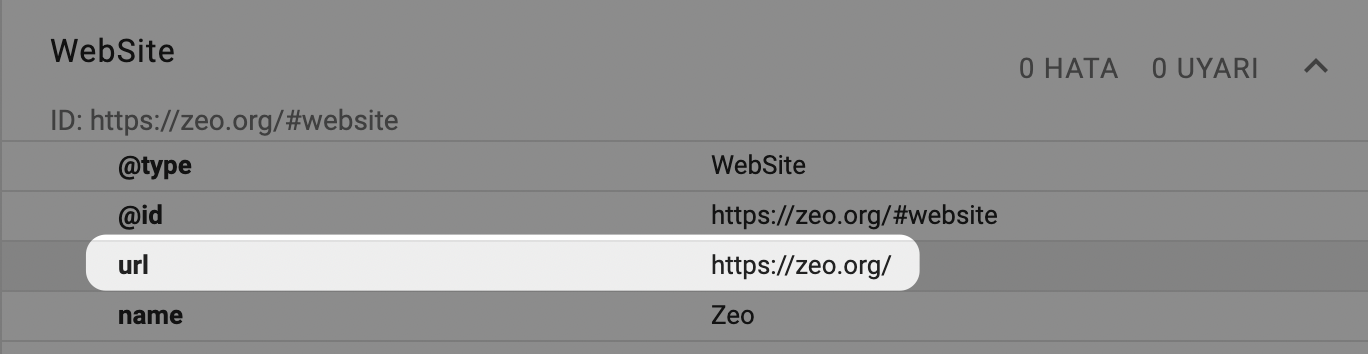
URLs in Structured Data
No matter which schema type you use, such as Article, NewsArticle, Product, or BreadcrumbList, you should check that the final URL of the referring URLs is included in the schema code. If you specify the old URL as the product URL in the Product schema, this may cause mixed signals to be sent to Google.
Duration of Referrals
When making your redirects, keep old URLs active for at least 1 year. Removing old URLs within a few weeks or a few months before Googlebot sees them can cause signals not to transfer and make it difficult for Google to understand the new page structure.
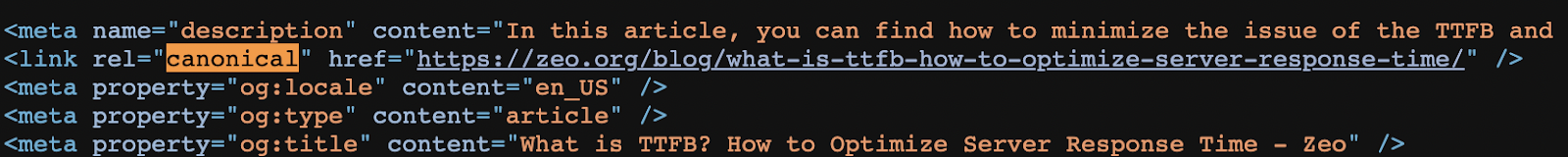
Canonical Errors
This can be a problem if URL A has a redirect to page B and page B's canonical points to page A. In these cases, Googlebot can use multiple signals to figure out which signal is consistent.
Using No Redirection at All!
I don't even want to think about not using redirects at all, but I wanted to mention it because I've come across it in the past. If you don't use redirects, users who come to your site through old URLs will see your 404 pages and will not be able to take the actions they want. Therefore, you may lose your loyal users.
As I conclude this article, I need to summarize that avoiding redirect errors is one of the important improvements that have positive effects on technical SEO and user experience.