SEO Guide In All Aspects for Beginners
Search: Where the questions meet with the right answer
a) Searching to Meet the Need in the Age of Information

What makes human beings different from all living beings that have ever existed in the world is undoubtedly our ability to think and question. As the only living beings capable of asking questions, human beings have applied many ways to reach the answers to her questions throughout history. Human beings who tried to find the answers to these questions through observation, in the beginning, accessed a completely different medium with the spread of the internet which emerged as a military technology in the late 1960s in the 1990s. Thanks to the large-scale developments in digital technologies, the internet has become the most important tool for people to find answers to all kinds of problems.
The production of content and information has reached the highest level seen in human history via the Internet, one of the greatest developments of our time. When we look at the internet consumption all over the world, although we consumed 1 zettabyte, (1,099,511,627,776 GB) content in 2016 (GB), it is expected to reach 2 zettabytes in 2019.
This phenomenon, which doubles its consumption in just 3 years, is becoming an even bigger part of our lives day by day with the diversification of smart devices. The effective communication tools of the past media, such as television and newspaper, expected us and forced us to consume the content presented to us in a passive role. However, with the introduction of the internet into our lives, we, as the user, have taken an active role and have become able to select and create our content. Although the growth in the internet area, where users can also produce content, seems to be beneficial in terms of increasing the diversity of information, it should be acknowledged that this brings some problems.
The Internet geniuses of the era saw that in a world where anyone can produce content, the percentage of quality information is rapidly declining and people have to struggle through a huge dump of data in order to reach the information they are looking for, aimed to contribute to the search for the information the users need by creating search engines. Of course, it is not possible to qualify all of these queries as searches aimed to reach only information. Nowadays, every one of us looks for all the information we want to get on the internet, from the faucet repair to the specifications of the new mobile phone we are going to buy.
The search, which is on the radar of many commercial enterprises with this aspect of it, is becoming more and more important. With the inclusion of social media, another important breakpoint of the internet revolution, in our lives, global figures show that searching is still the most popular method used by people to reach one site from one site to another even though its percentage of influence in the total market declines slightly. While the development of the search has made us individuals who can access information with less effort, companies have started to look for different methods to benefit from the new situation that has arisen from the growing interest in this area.
This quest for different methods has led to the emergence of processes such as SEO, which covers all the tactics used to rank high in the search engines (Search Engine Optimization), and PPC, which covers paying fees per click to take part in sponsored results (Pay per Click),
b) Where Queries Meet Results: Search Engines
Yapılan araştırmalar arama motorlarında her gün yaklaşık 8 milyar sorgu yapıldığını gösteriyor. *Research shows that around 8 billion queries are made every day in search engines. *To be more precise, we can state that more than one daily search per person or more than 8,000 searches per second is made, when we take the quantity of world population into account.
This is a fact that shows what great work the search engines accomplish. For all these reasons, search engines are pushing the limits of their material and human resources to provide the most accurate, the most detailed, and the fastest response to their users. This means a significant investment both in time and in financial terms.
Of course, while the search engines offer people the information they are looking for free of charge, the return of their investment must be met by advertising models based on sponsored results. However even if they are advertisements, search engines are obliged to keep these fields answering appropriately to what users are looking for. We know that the first project realizing the potential of search engines was Archie, which was launched in 1990. Archie's main mission was to provide other users with lists of files that were found in the FTPs (a kind of file sharing protocol) of various websites at the time.
This search engine, which works on a very basic level and only by listing method, is the first search engine due to its vision and structure. After this project, they realized that search engines became a necessity. At that time many companies have invested in this field to seize the opportunity but none were as successful as the Altavista which started service in 1994. Many search engines wanted to put the web together in their index during the period when Altavista was strong. In this period having a search index of even 2 million was very impressive, while AltaVista included every corner of the internet in its index of 20 million. Altavista, which had a much more impressive ranking algorithm than its competitors as well as having higher data access, had achieved a great acceleration in a short time.

Yahoo! was undoubtedly one of the most important names known to everyone who spent time on the Internet, along with Altavista. Known as the closest competitor to Altavista, the strongest name of the time in the search market, Yahoo was also very strong as a web portal. In particular, it held a significant portion of the traffic of the period through services like Yahoo Mail and Groups. This competition would come to an end with the arrival of a newcomer to the market weakening both competitors and ultimately with Yahoo's acquisition of Altavista much later.
In 1998, even though Yahoo, Altavista and Ask.com held a serious dominance in the market, the era of Google had already started with its technology leaving most of its competitors behind. In the era when the web grew rapidly, Google, which outperformed its competitors with its creative solutions for creating a wide index, published an article about PageRank algorithm in the same year. The article titled The PageRank Citation Ranking: Bringing Order to the Web was aimed at finding a solution to the fundamental problem for the search engines: to determine the rankings! Google, which already has a broad index, suggested that the links that websites provide to each other should be considered as a ranking factor. The value of an academic study was already measured by how many scientists it quoted. Google was able to effectively adapt the system to the web where, unlike academic journals, everyone produces content freely and this resulted in a significant increase in ranking quality.
Moreover, according to this system, the links coming from web pages with high authorities provided a much greater effect since not only quantity but also the quality was measured. In 1999, Google Inc, which was not a company yet, became a corporation with the first angel investment of David Cheriton, one of the Professors at Stanford, started to grow rapidly.
After AOL, one of the major portals of the era selected Google as their search partner in 1999 and Yahoo did the same in 2000, Google's inevitable rise started in its entirety.** As we only have a few years left before we celebrate Google's twentieth birthday, Google’s rise in the market continues to rise. According to Comscore data, it holds 64% of the US market, and according to the Gemius data, it holds 95% of the market in Turkey. In addition, except for China, South Korea and Russia, where it encounters difficulties to enter due to legislation, Google is the leader in all markets it exists in.
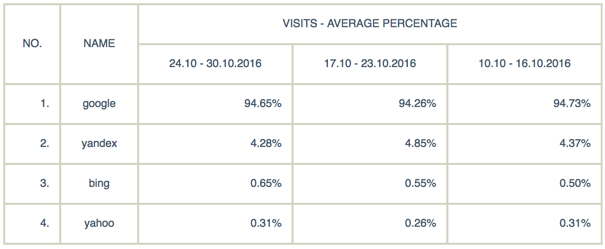
(Arama motorlarının Türkiye’deki kullanımlarına ait yüzdelik dağılım) Bugüne değin, arama motoru pazarında birçok oyuncu belirli dönemlerde yükselişler yaşayıp daha sonra bunu yitirse de yenilikçi yaklaşımıyla Google, kurulduğu günden itibaren güç kazanmaya devam etmiştir. Eğer internet dünyası yakın gelecekte büyük sürprizlerle karşılaşmazsa, aramanın lideri uzun bir süre değişmeyecek gibi görünüyor. * Enge, E., Spencer, S., & Stricchiola, J. C. (n.d.).
The Art of SEO: Mastering Search Engine Optimization (3rd ed.) ** WordStream, “The History of Search Engines - An Infographic“, http://www.wordstream.com/articles/internet-search-engines-history (Percentage distribution of search engines’ usage in Turkey) Heretofore, the market of search engines many players have temporarily risen in certain periods and then fell, Google continued to gain strength since its inception with its innovative approach. If the internet world does not face any big surprises in the near future, the leader of the search will not change for a long time. * Enge, E., Spencer, S., & Stricchiola, J. C. (n.d.). The Art of SEO: Mastering Search Engine Optimization (3rd ed.) ** WordStream, “The History of Search Engines - An Infographic“, http://www.wordstream.com/articles/internet-search-engines-history
c) Users’ Interaction with Search Engines
As a result of searching and asking questions, all humans want clear answers and satisfying information. As a response to this demand, search engines try to get us to the right information either with the sites that they list in the top ranks or with their answers without directing to a website. The technologies used to provide the right answers to the questions we ask the search engines to improve from year to year. For example, although Google’s voice recognition technology was not uncommon in Turkey and many of the queries made from mobile were shorter and results-oriented searches in 2014 and earlier, today it is possible to reach correct information with much longer queries through voice search. The tools we use to make calls are not limited to our computers or smartphones. Wearable smart products and smart home systems, which are coveted by many tech giants nowadays, will also be among the tools we will search frequently in the future.
According to Morgan Stanley's report, by 2020, 75 billion separate devices are expected to be connected to the Internet in the world. With such diversification of tools we can search from, it is clear that we will all continue to satisfy our need for information from search engines. The experiences we have almost every day show that the days when the search engines listed only 10 blue links are over. We all know that search engines are no longer working simplistic enough to only check how many words are in the article when evaluating the content.
The search engines that are qualified to do assessments only on syntax (syntax) are left back in the 2000s. Nowadays, we can see that there is a semantic approach that tries to capture meaning by evaluating the interrelations of words and sentences. In other words, Google wants to be able to perceive the implications a human brain obtains when it reads the content. To get to comprehend this concept more clearly, let's proceed over an example and ask Google where was our company Zeo (formerly known as SEOzeo) founded.
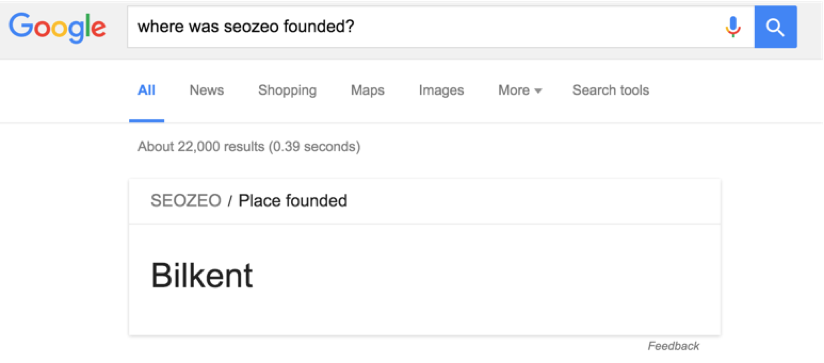
Google can easily answer that the founding location of our company center was a technology development center in Ankara Bilkent after querying on Knowledge Graph (ie Knowledge Graph). This simple example shows what kind of policy do search engines follow for responding user requests in information-driven searches. Let's have another example, from e-commerce sites this time, and take a look at the searches for a popular phone, the Samsung Galaxy S6 Edge. First, we need to understand which information does a user who searches for "Samsung Galaxy S6 edge" wants to reach:
-User may be doing a preliminary survey to obtain information about the product,
-User may want to get to the product page on Samsung's website,
-User may have made her final decision and may want to buy the product,
Accordingly, Google should provide a search result page that can meet the three different needs of users. If the searcher doesn't provide clear detail in her search engine query, Google usually selects 10 results to answer all the concerns and interests. It may be possible to approach Google's search results more critically by learning these search types, details of which will be discussed in the following sections. As professionals in the digital marketing world built on the basis of making more effective metrics with big data and figures from beginning to end, we often ignore the people behind these figures.
According to a statement made by Google during the announcement of the artificial intelligence-supported search algorithms named RankBrain, about 15% of 3.5 billion searches made every day are in terms that have never been searched on Google before. Being able to produce so many unique queries that haven't been included in nearly 4 trillion searches made so far makes us question the limits of human creativity. Even this data by itself proves how small a set of data we are looking at during the process to identify the right keywords. Therefore, the basis of a good SEO strategy should not be based on keywords, but be based to provide an insight into the needs of users. Getting to know your target audience and creating a website that can produce the right answers to their queries is one of the basic requirements of SEO.
d) Correctly Interpreting the Needs of Users, Understanding the Intent
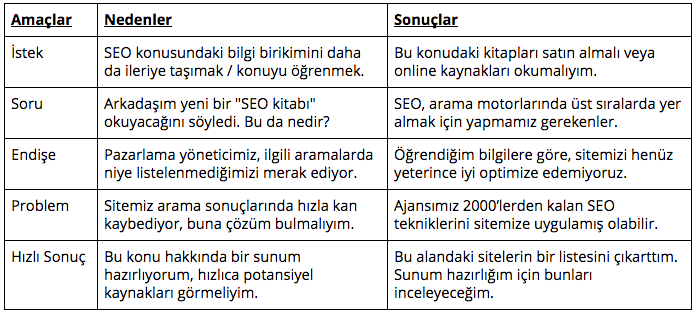
To establish a good SEO strategy, first of all, it is necessary to know the target audience of the website and keep in mind the fact that the searchers are real people. Understanding the basic need behind the search of users within your target audience is one of the most discussed topics of SEO-themed conferences today. As stated in the presentation of Marcus Tober, the founder of Searchmetrics, one of the world's leading SEO data providers, during our SEOzone conference in 2015, each user searches for a reason. Searchmetrics has classified these reasons into 5 different subsets based on the analysis of billions of keywords it tracks:
- Requests: The user may wish to satisfy a need through the search engine. If we go over the previous example, "samsung galaxy s6 edge" the user searching on may wish to place an order directly.
- Questions: One of the most common types of searches is the query that people make to clarify the question marks in their minds. If the user wants to know the price of the phone, he will search for that.
- Concerns: The user performing the search may want to address a concern. Following the same example, the user who plans on buying the phone may not be sure whether the product will meet his needs in terms of data storage.
- Problems: If the user who purchased the phone had an issue when using the product, he or she may want to search for a problem regarding this issue with Google to investigate how other users have found a solution.
- Smattering: Users who want to easily access any information about the product can be found. For example, a user who is curious about the price range of the product can make a "samsung galaxy s6 edge price" search, preferring to quickly browse the prices in the ads and leaving the page without clicking.
Here we can see that each type of user can have different purposes for searching. We have seen above that each user may have different reasons to search. Therefore, when they complete these searches, it is not difficult to guess that there are different results that they all want to reach. To evaluate the issue clearly and look at it from a different angle, let's quickly reassess it over a non-commercial search query. For example, let's take one of the searches that may have directed you here, the "SEO book" search: Based on these scenarios, it is possible to analyze your user's intentions to produce the right answers for them.
We should not forget that search engines are interested in bringing the most relevant results to the queries users are looking for as we do. In addition, they find the content that best suits the needs of the user in half a second and present them in order of relevance among the index of 60 trillion pages. If the search engines, led by Google, fail to meet the needs of their users, they may face the threat of losing market shares. For this reason, they always want to bring the best results to their users in the field of organic search results.
i) Properly Classifying Queries of Users
We always believe that providing the best answer to the questions users ask is our priority as ZEO. So in this section, we first discuss what users may aim to find within a page. Do these users use queries that reflect their purpose when making relevant searches? One of the most widely accepted opinions for the classification of keywords is that we can muster all keywords in three different groups:
- Informational queries, Searches to access information.
- Transactional queries, Searches with a commercial value.
- Navigational queries, Searches with a predetermined orientation.

The better you understand the keyword groups, the more effective you can make your priorities when creating your SEO strategy. Informational Queries: Searches that aim to access informative content on any subject. When we consider all search engines, this is the dominant and the most diversified search type of the internet, although a clear statistic does not exist. The reason why this type of search has such a large volume is that there are no limits on people's search for answers to all kinds of questions and the desire to access new information on the internet. In order to better understand and internalize the subject, let us consider some searches that a professional who wants to improve himself in SEO can make during the day:
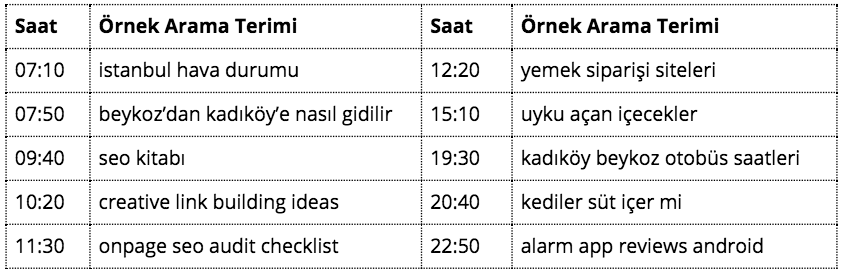
There are always great opportunities in this type of search where the main goal is to reach information. Although it may look like that these searches do not create purchasing tendencies at first glance, profitable results can be obtained through communication with a user whose needs are analyzed correctly. For example, the user asking for the weather and directions before going to work might choose not to click on any site, as she receives the answers to the question directly via Google services. This may be classified as an information-driven search that does not provide any conversion. Of course, we have examples of information-oriented searches that can lead to sales conversions. For example, suppose a user searching for an "SEO book" is really satisfied with the site she clicks on in the relevant results listed. If the site had generated a strong content in terms of SEO, we can be sure that the consultancy service of this site will attract the attention of the user / customer in the medium to long term.
On the other hand, a user looking for ideas for link building might want to buy it if she has seen a comprehensive training set in this field. Or a consultant looking for a checklist to identify missing points in his SEO work may consider purchasing one of the report kits of another consultant with a highly successful career in the field. Although information-oriented searches do not have as much potential as commercial queries, these can be turned into a high advantage with their high search volumes and easy competitive advantages from their diversity.

Navigational Queries: Searching habit is undoubtedly one of the most important building blocks of internet culture. Instead of the address bar that we used in the past years, we can easily reach any site through the search engine by simply typing the brand name. We can simply define the way we use to access Facebook through our desktop devices and our searches as navigational queries. Navigational queries don't always have to be directed to the homepage of a website.
Searches that include the site / brand name, as well as the associated page, are called precision navigational queries. For example, the search for “Zeo's SEO book” on this page can also be considered a navigational query. In order to understand the situation more clearly, let us repeat our example from a professional who wants to improve himself in the SEO field:
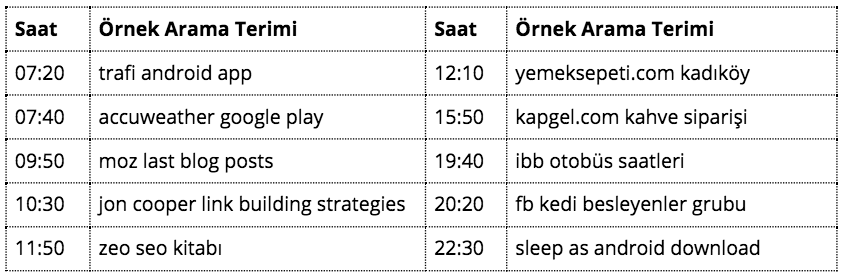
The conversion rate is very high because all navigational queries are based on users who know what they want or referrals. However, the only possible way to get effective results from being listed in the results of such searches, unfortunately, comes from the navigational query being directed to your site. In other words, it is almost impossible for Zeo to rank high in searches related to the SEO book written by Moz.com. Even in the case of such a scenario, it will not take long for the searcher to understand that the first result does not directly address them, because they know what they want. Therefore, in such a case, a very weak traffic gain occurs.
However, getting a lot of traffic in this type of phrase for recognized brands doesn't necessarily mean that we'll always earn sales conversions. We can continue through the examples above.. KapGel, a cargo order / courier application, may not have the desired sales conversion if they direct users to their homepage when responding to a search (kapgel.com coffee order) related to coffee order. It is normal to have a difference in the reactions of a user who can find out from which coffee chains they can order by using KapGel, and a user reaching their standard home page. In this scenario, we see that the company needs a page that will convince you to order coffee by installing their app. Although the user has made this query by wanting to reach that page, such searches will require good content and user experience to keep bounce rates to a minimum and increase conversions.

Transactional Queries For many brands, the most important target in SEO is the transactional query. You should not think that the result of this search is purchase as a result of the connotation of the name. While the most important interaction goal for many companies is online purchasing, the most important conversion for the sale of a housing project can be the form being filled by a prospective customer who wants to know about the details before the purchase.
A query does not always need to be close to a financial outcome to be transactional, for example, a site may have to focus all its objectives on increasing the number of active participants even though there is no income model like Quora, the world's largest question-answer center. What is meant by the interaction here is actions that are purely aimed at the company's goals and the results it seeks to achieve. To better assess this, let's take a look at all the sample interaction searches an SEO consultant makes during the day:
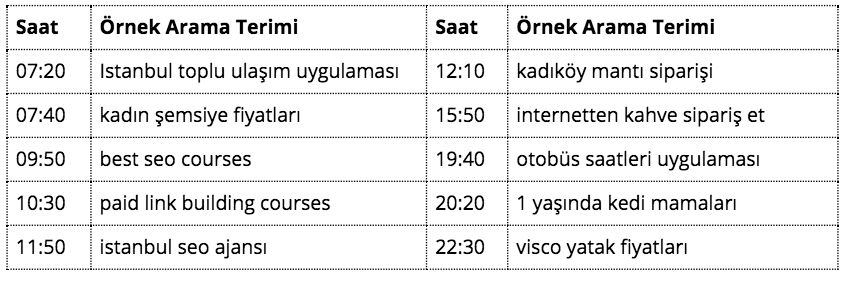
Transactional queries, which have a high commercial potential for the business, can be confused with information-driven searches in many cases. When we see the point that content marketing has reached today, it is an indisputable fact that users seeking information are one of the most important feeders of the purchasing funnel. However, if you want to get quick conversions by generating traffic to your existing pages without creating new pages, you should focus on highly competitive phrases.
At the same time, according to the world average, the most expensive phrases that you can buy in AdWords are transactional phrases. To present an example of the tendency of these groups for conversion, we can easily understand that a user searching for "visco bed prices” just before going to bed is not satisfied with his bed and is thinking to buy a new bed. SWOT Analysis: Strengths and Weaknesses of Keyword Groups We now know that all searches on the Internet can be reduced to three different categories. Understanding these groups correctly and effectively internalizing them will help you to understand SEO correctly in the future. Since being able to distinguish what the purpose of a query is for as soon as you see it will be one of your most important assistants in the keyword research process, let us first evaluate all our examples together:
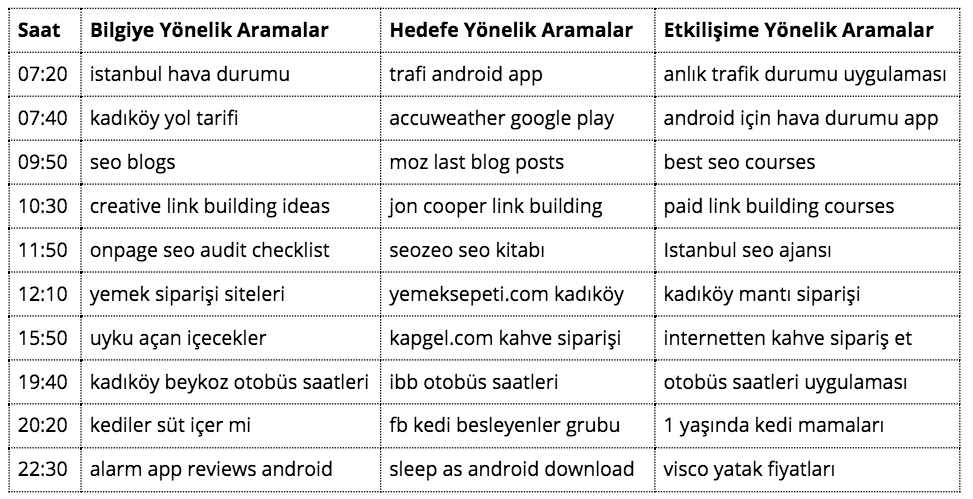
When we evaluate them side by side, the distinctions between different variations of queries close in meaning can be seen more clearly. Once we know which category type a query belongs to, we need to be able to correctly understand what these categories mean to us. SWOT analysis, which is one of the most preferred methods of business investment analysis, presents the strengths and weaknesses of a subject together with opportunities and threats. A similar analysis of the above-mentioned categories is also possible in SEO:
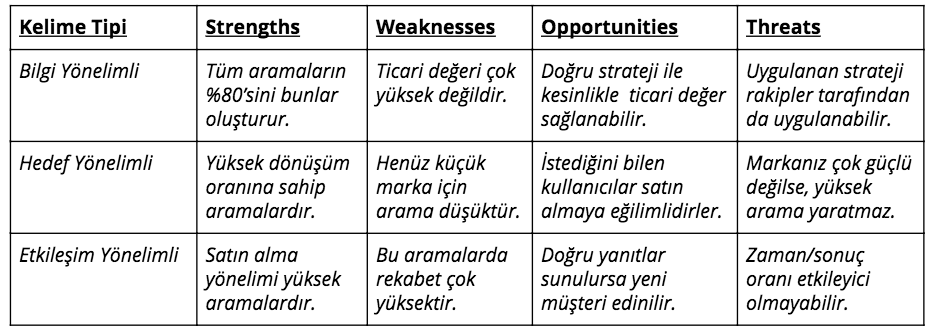
According to this analysis, predominantly information-oriented searches seem more logical for a small brand, while a strategy for interaction-oriented searches can also be developed. However, you may want to consider optimizing for targeted searches if you are developing an SEO strategy for a major airline, including the brand name. We will elaborate on Google's approach to this topic in the section on keyword research.
ii) Interpretation Systems of Search Engines for User Queries
As you can see in more detail in the next section, the first step of Google search is based on assigning a meaning to the search query you make. Specifically, Google has completely changed the way it perceives and evaluates queriesInterpretation Systems of Search Engines for User Queries. At the SMX West conference in California held on March 1-3, 2016, Paul Haahr, one of Google's engineers in charge of search ranking, made one of the most informative presentations on search signals, presenting the most detailed information by Google's search team about them.
When you perform a search on Google, your query is subjected through two processes named Query Processing and Query Understanding. During Query Processing, all semantically related words are listed and put together. Google's semantic weighting engine is being used here for correct weighting. (I suggest you review the link for the detailed diagram) So when you produce content related to the White House, Google can understand this only through the semantic relationships established with phrases like Washington or US President in the content. As a natural consequence of this, achieving success in 2018 using the SEO techniques of the 90s and repeating the words “White House” over and over has become very difficult.
On the other hand, when you perform this search as a user, Google can easily understand whether you're talking about a white house or the White House as a private name - based on your previous searches and general user habits, and thus set all rules accordingly when searching in the index.

When the processing process is over, the existing query needs to be expanded to make sense. During Haahr's presentation examples of gm trucks and gm corn are given. While gm trucks mean trucks produced by General Motors, gm corn means genetically modified corn. In both cases, the abbreviation GM, when taken in conjunction with the following statement, creates sub-searches with meanings that are completely different. Google brings you the results you want thanks to these processes which take place in a few milliseconds, with its effective evaluation of user data and web index it accumulated since its inception.
iii) Understanding User Needs Through Present Day Search Results
We now know that Google has a fairly broad semantic index to make sense of our searches. On the other hand, we know all three groups that we will use to understand the intent of the queries made. Now, let us examine how does this information we learned the theory of actually affects search engines:

In the table above, you can see the results of all search types and their categorization. We have classified the results listed by Google into 4 different categories based on the search types we mentioned earlier.
If we evaluate all the results one by one:
Encompassing Search: This search, which can be considered information-oriented according to the standard classification, is actually encompassing because it holds many requests together. A user directly searching for "samsung galaxy s6 edge" can have many purposes, such as acquiring information about the product, or buying it. In another scenario, the user is already the owner of the product and may be searching for the official website of the product manufacturer. In the worst case, a young tech enthusiast who may be curious about the appearance of the product may have carried out this search. When we look at the table in its entirety, three Google ads, one quintet product ad and six different e-commerce sites listed in the organic market can prove that most of these queries were intended to purchase the product.
Again, the two manufacturer sites were probably listed in order to respond to the users seeking support for the product. An information and experience sharing site in this example was directly included in the results to address the user seeking information on this subject. Even though we can make these manual classifications and express our approaches to these queries, we must state that it is not easy to give such detailed responses to every request when we consider that all rankings on the web are automated.
Therefore, when you create pages for inclusive queries you need to focus on creating page types that can meet multiple needs of users. In the search example above, Hepsiburada’s first ranking probably originates from the opportunity to purchase the product from its stock and more than 10 different vendors, hosting more than 100 comments about the product, introducing the product with the content produced directly by them, and providing the video of the product, thus presents a richer content and buying experience to the users compared to its many competitors.
Informational Queries : In this query, we see that the "samsung galaxy s6 edge reviews" page lists the review sites and comments on the official site where you can directly access product-related reviews. So Google understands that we need to reach comments from experienced users when we made this query and gave priority to video reviews and sites with user reviews about the product. The point we must pay attention to here is that Samsung takes first position here by using both its domain authority and the power of comments via the comments section created on its website. It is a very valuable achievement for a brand to rank at this level when they house their product reviews on their site on this channel.
When we examine this query in detail, we see that nine separate answers are from experience review sites and that one answer is from the product listing page on hepsiburada.com. Here again, if we consider that hepsiburada.com houses the content of comments on the topic in the strongest way compared to similar competitors, we can comprehend why an e-commerce site is listed in a query related to comments easier.
Transactional Queries: In this search type, we will be analyzing one of the most ambitious queries "buy samsung galaxy s6 edge". Since this search includes a direct purchase phrase, we can see the dominance of e-commerce sites in Google’s approach to what will match best to this query from the green color in the table. After we consider that red marked ads are purely commercial sites, we see that Akakce.com, which is a price comparison engine, is marked with blue color (also possibly considered as e-commerce) and it is here because it provides information about the product. In addition to the Akakace.com result from this query, even though it is not a direct purchase site, the Samsung official site appears to be listed in the results as includes a list of official resellers, thus providing the right referrals for the buyer.
Navigational Queries: Even though targeted calls for the mobile phone industry is query that won’t be encountered very often, it is one of the types of queries we should examine. A user who wants to search within Samsung's site can query for "samsung.com galaxy s6 edge" on Samsung's site to reach the most relevant pages of the phone. In this case, the results that we expect almost overlap with the results we receive, and all results are directed to the site of Samsung while being listed in lilac color All of the cases above provide good tips on how far Google has progressed about measuring our search intentions. Creating an awareness that will interpret the results of all your queries to produce the pages that can provide users with correct answers by interpreting each query type and Google's responses to these queries during SEO efforts will provide added value to you and your organization.
iv) The Future of Search: Interconnected and Communicable Queries
A fact that everyone agrees on is that in the field of understanding search queries Google is one of the most powerful companies in the market today. Thanks to developing technology and machine learning, we are now waiting for Google to go beyond understanding our queries and start to engage in dialogue with us. While writing this book let’s take a brief look at this situation, which can be seen in very few queries in our year of 2016.
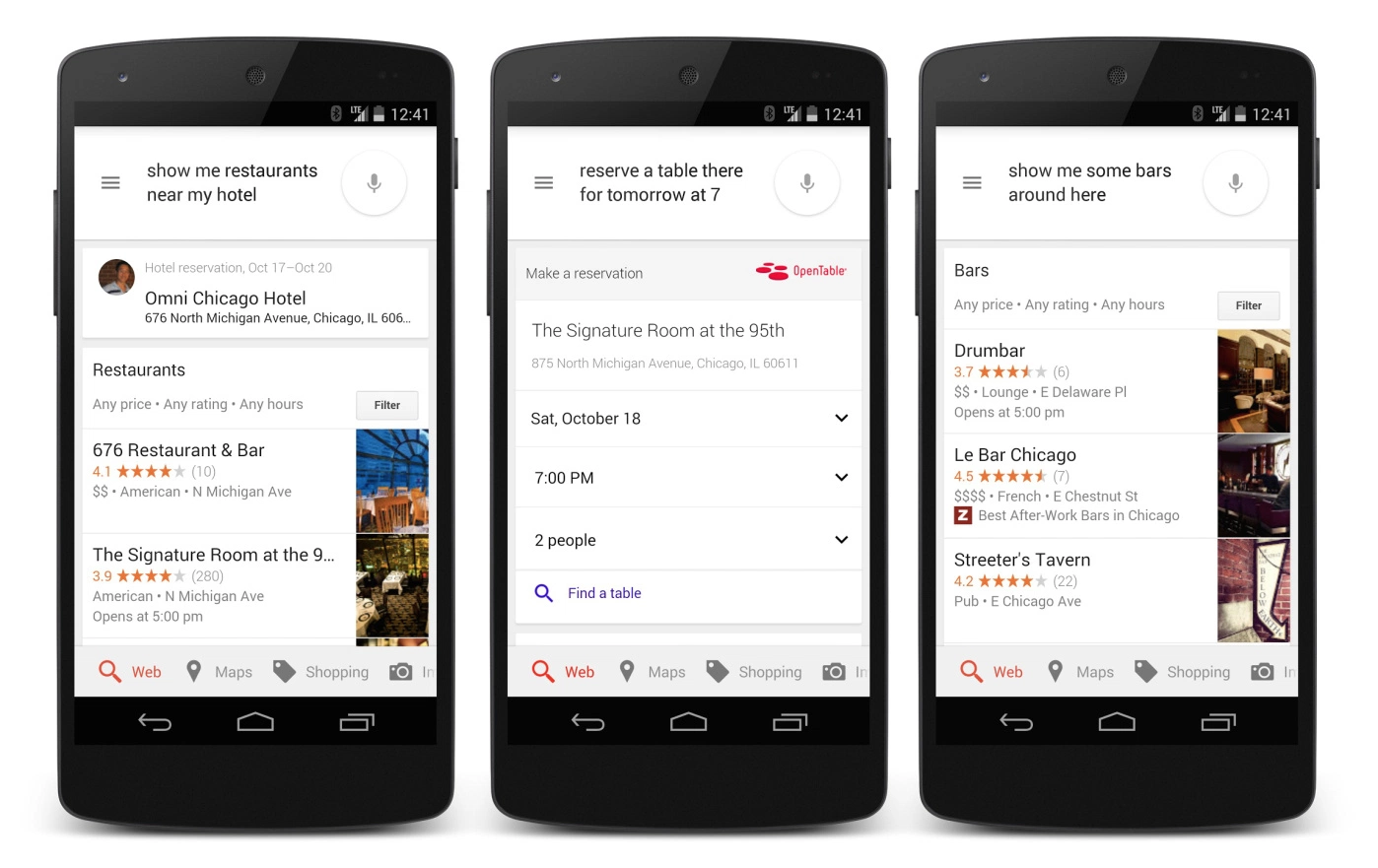
Let's assume you're in Seattle to attend MozCon, an SEO conference. This is the first time you've visited the city, you search for restaurants near your hotel to eat something after the conference. At this point, Google already knows the exact location of your hotel, as the confirmation email for your reservation from Booking.com has been sent via Gmail. Using this data, the hotel lists all restaurants within a radius of 1 km. Immediately after choosing a restaurant here, you want to reserve a place for 7 tomorrow evening. Your reservation is made automatically through the OpenTable system, which integrates many topclass restaurants in the USA. If you want to have a drink when you leave, you can quickly get a response by asking for the bars close to the restaurant.
All of the search queries we see in these examples are information-oriented searches. But the most obvious difference between them is that you don't have to specify around which hotel you look for a restaurant or around which restaurant you look for a bar making these interconnected queries. While this technology, which is still under development, does not produce very good results for Turkish at the time of this book's writing, it is not difficult to foresee that there are computers and people who will communicate with each other in the future when we look at the historical development speed of Google.
e) Understanding the Nature of Revenue Models Arising From User’s Needs
Although the search engines are committed to ensuring that users reach the most accurate results in the fastest way completely free of charge, they have to develop an income model to balance their consumption of material and human resources. Of course, at the top of these revenue models is search engine advertising.
When we look at historical development, it's surprising to see that many search engines rent banner ads, even pop-ups for all search results pages. Adwords, the innovative revenue model offered by Google, has impressed all competing search engines with its vision. With its Pay-per-click (PPC) system, advertisers pay for each visitor who comes from that specific keyword search by participating in a multivariate auction in the words they set. When discussing the fundamentals of AdWords, which will become Google's revenue model, in their doctoral dissertation on the PageRank algorithm, Google founders Sergey Brin and Larry Page at Stanford University state that their most important resource, in the long run, is the advertising model. You can read how the quotation of the dissertation quoted below conveys their thoughts from 20 years ago:
“Currently, the predominant business model for commercial search engines is advertising. The goals of the advertising business model do not always correspond to providing quality search to users. For example, in our prototype search engine, one of the top results for cellular phones is "The Effect of Cellular Phone Use Upon Driver Attention", a study which explains in great detail the distractions and risks associated with conversing on a cell phone while driving. This search result came up first because of its high importance as judged by the PageRank algorithm, an approximation of citation importance on the web [Page, 98]. It is clear that a search engine that was taking money for showing cellular phone ads would have difficulty justifying the page that our system returned to its paying advertisers. For this type of reason and historical experience with other media [Bagdikian 83], we expect that advertising funded search engines will be inherently biased towards the advertisers and away from the needs of the consumers.”
Google launched in 1998, and after its advertising model Adwords is implemented in 2000, this model has grown rapidly, becoming one of the largest advertising platforms available. The basic task of this system, which was created with a very simple working principle, was to combine advertisers and users by presenting the results related to the searched words. Usually located at the bottom and top of the Google search results page, these ads account for about 90% of all Google's revenue. In this respect, Adwords, which is a very valuable revenue channel for Google, is still one of the biggest items in various brands' budgets for many different channels, from new product launches to traditional advertising.
On this platform, where different participating companies compete in an auction for certain keywords with their maximum bids, bids reach well above $ 100 per search on some searches with very high commercial value! For this reason, we should not be surprised that banks will increase their bids in sectors where all banks compete mercilessly - such as home loans / mortgages or vehicle loans - depending on the potential earnings they may earn from the sale of the loan. Or, in costly healthcare operations such as hair transplantation, we can see figures that can compete with the credit sector, especially in the US market.
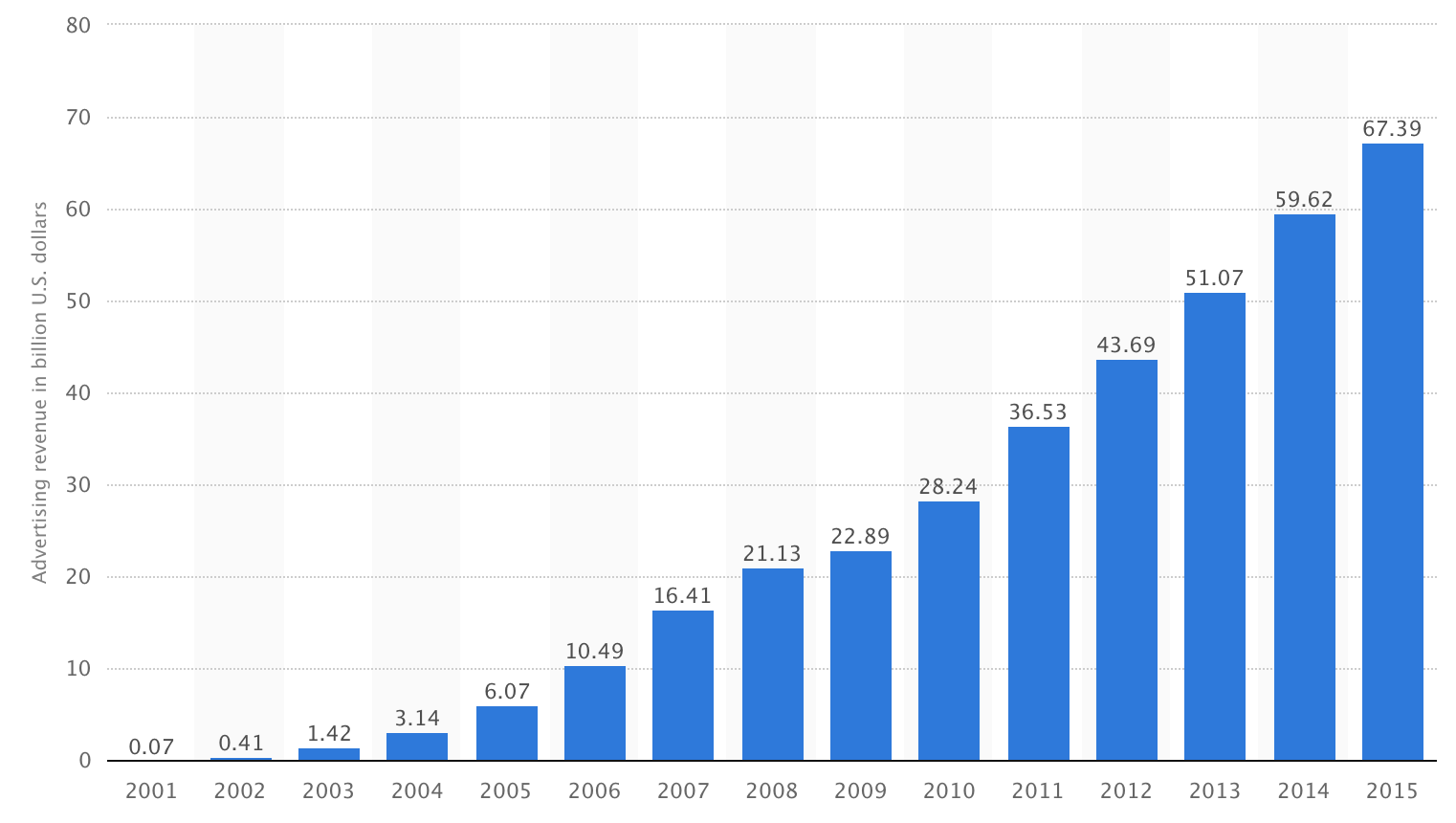
According to this survey published by Statista, Google's total advertising revenue in 2015 is estimated to be around 68 billion USD. While Google acquires revenue from advertising as a business, the trends in organic search results do not match the ad results, and there are significant differences in clickthrough rates. The main reason for this is that Google's enhanced matching algorithm is improving day by day and users have more confidence in organic search results. Of course, we can also state that the rate of clicks on organic results is high due to the more satisfactory response in terms of content and user experience that can be found in the organic results of the query. If we must examine in detail using the data from many different research companies; (***)
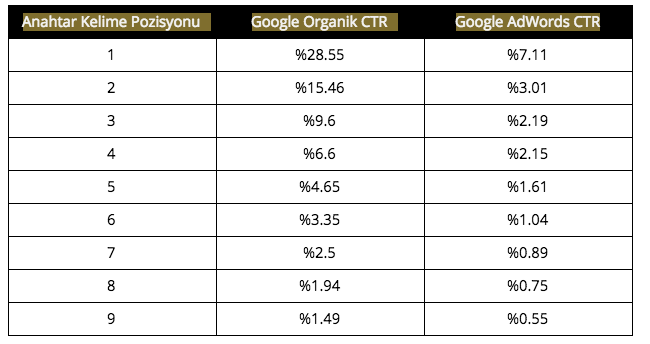
As can be seen from the results, even though users prefer to click on organic search results, Google AdWords is one of the healthiest marketing investments that many companies can make. The main reason for this is that traffic is charged only if the user is directed to the website by evaluating the data in a fully measurable way. Although it is beyond the scope of our book, it may be useful to know this model at least tangentially to better understand Google's analytic approach.
Although it is commercial, the model produced by Google for PPC advertising has inspired many business models since its implementation as a very ambitious model of keeping the user as the priority. For example, if you try to sell home loans by advertising on a search for flowers, you may have to pay very high costs for this ad because your ad page has very low relevance to that search. Adwords Quality Score, which reflects the value of your page, its associated search, and your overall site quality, is one of Google's most important advances in the advertising model to protect its users and remain a mystery to many companies. Contrary to a widespread opinion, there is also no correlation between your AdWords advertising budget and your success in your organic search results.
Although such an opinion is common in Turkish webmaster communities, many data providers serving worldwide today show that even brands that spend millions of dollars on AdWords budgets every year can have very poor organic search performance. ****https://www.advancedwebranking.com/ctrstudy/ , http://www.accuracast.com , http://www.wordstream.com/average-ctr , https://chitika.com/google-positioning-value